U.S.-made perovskite-silicon tandem solar modules could be produced at around $0.35/W
Techno-economic analysis conducted by NREL researchers has shown how perovskite-silicon tandem solar modules could currently hardly compete in cost with incumbent PV panels. Production costs for U.S.-made tandem products were found to range between $0.29/W and $0.42/W, with module efficiencies ranging from 25% to 30%.
Ensuring sustainability in solar and battery storage supply chain
Geneva-headquartered dss+, a spin off from DuPont, helps industries switch to sustainable and resilient operations. It serves power and utilities, oil and gas, metals and mining, among other industries.
With a strong presence in India alongside leading industry players, dss+ has been instrumental in shaping the region’s energy landscape. Srinivasan Ramabhadran, managing director, APAC, dss+, speaks to pv magazine about balancing efficiency, cost, and environmental impact in solar and battery storage manufacturing.
Spontaneous glass breakage on solar panels on the rise
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory noted an increase in spontaneous glass breakage in solar panels. The PV Module Index from the Renewable Energy Test Center investigates this and other glass-related trends in solar manufacturing.
Weather-related damage to solar assets in USA exceed modeling expectations by 300%
The report from kWh Analytics, with input from several industry leaders, identified 14 risks to be aware of in the solar industry, including risks related to extreme weather, such as hail, and operational risks.
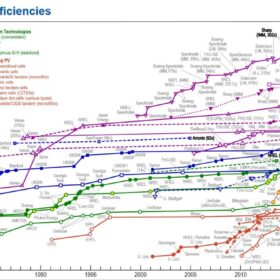
NREL interactive chart of solar cell efficiency now including ‘hybrid tandems’
The new cell category includes perovskite/silicon, perovskite/CIGS, III-V/silicon and perovskite/organic tandem PV devices. It will list the absolute record efficiency for all-perovskite, two-terminal tandems regardless of the number of junctions.
US government funds pilot project for heated sand energy storage
The US Department of Energy is funding a pilot project to demonstrate the commercial viability of storing energy in heated sand, which is capable of producing 135 MW of power for five days.
Perovskite thin film: Out with the old, in with the new
Silicon-perovskite tandem solar requires optimization of both approaches, and embodies the weaknesses of each. Meanwhile, the use of pure thin-film devices offers a cheaper, simpler, and more sustainable PV solution for the United States.
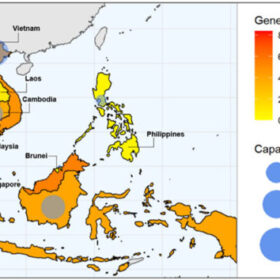
The potential for floating solar in Southeast Asia
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and its partners have assessed the technical potential for floating PV throughout Southeast Asia.
All-perovskite tandem solar cell with 27.1% efficiency via gas quenching
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has achieved remarkable efficiency and stability for a wide-bandgap all-perovskite tandem solar cell. The scientist developed the device with an inverted architecture and used gas quenching instead of an antisolvent in the manufacturing process.
Cooling down solar modules by increasing space between panel rows
A US research team claims to have demonstrated that increasing the spacing of solar panels between rows improves PV system efficiency and economics by allowing airflow to cool down the modules. The method could improve a project’s LCOE by as much as 2.15% in certain climates.