The impact of module pricing on solar project viability: Trends and predictions
India’s solar sector faces rising module costs due to recent developments, including the imposition of anti-dumping duties on solar glass and China’s reduction in export rebates on solar modules, impacting project viability. These shifts underline the delicate balance between promoting local manufacturing, pursuing geopolitical strategies, and navigating the economic realities of global trade.
CleanMax, Toyota Tsusho partner to develop 300 MW renewable energy projects for Japanese corporates in India
CleanMax has partnered with Toyota Tsusho India Pvt. Ltd. (TTIPL) to drive clean energy adoption among Japanese corporates in India. Together, they aim to develop and operate 300 MW of renewable energy projects by March 2028.
Why solar power can’t just be industries’ CSR afterthought
Companies that treat solar as a core part of their energy strategy, rather than a side initiative, often see these benefits play out with striking clarity. The investment case is strong. In most cases, payback happens within five to seven years. After that, solar becomes a net-positive contributor to the balance sheet.
Photovoltaics vs. photovoltaic-thermal
Researchers in India say that photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) systems offer greater performance stability than conventional PV systems in hot climates. Using irradiance and temperature data, the team applied a Random Forest model that predicted efficiency classes with 97% accuracy.
Adani commissions off-grid 5 MW green hydrogen plant
Adani New Industries Ltd (ANIL) has launched a 5 MW green hydrogen pilot plant in Kutch, Gujarat. Powered entirely by solar energy and backed by battery storage, the plant runs fully off-grid, marking a new step in decentralized, renewable hydrogen production.
Waaree Renewable Technologies secures 100 MWp solar EPC project in Vietnam
Waaree Renewable Technologies Ltd has signed a non-binding Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Viet Khanh Joint Stock Company to execute a 100 MWp solar PV power project on a turnkey engineering, procurement, and construction (EPC) basis in Vietnam.
The role of advanced transformers in India’s green transition
Without resilient, responsive, and renewable-ready transformer networks, India’s decarbonization goals risk being destabilized by the very variability they aim to harness.
New study estimates India’s solar potential at 10,830 GW
A new study by The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) has estimated India’s total solar potential at 10,830 gigawatts (GW), significantly higher than the previous 2014 assessment of 748 GW by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE). The study revisits conventional solar deployment areas such as barren and unculturable lands and explores additional avenues to expand the country’s solar potential.
Raminfo secures INR 474 crore rooftop solar order from RRECL
The project involves the design, supply, erection, testing, commissioning, and 25-year comprehensive operation and maintenance of rooftop solar systems with a total capacity of 73 MW. These systems will be installed on buildings owned by the Rajasthan State Government and its undertakings.
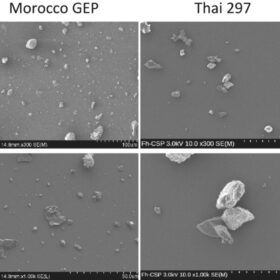
Different dust, different impact on PV module performance
Scientists in Germany have collected dust from Qatar, Morocco and Thailand to analyze the impact on the performance of uncoated solar glass and uncoated PV mini-modules. Their analysis has shown that dust coverage could range from 4% to 60%.