Inside the PV recycling black box
How PV modules are treated at the end of their life is an increasingly important issue, but some recycling practices leave a lot to be desired. Scott Azevedo from Intertek CEA explores how asking the right questions, paying closer attention to end-of-life treatment, and steering volume toward good recyclers can have positive long-term consequences for the solar industry.
TEXMiN, Russia’s GIREDMET ink pact on rare earth and critical mineral technologies
The TEXMiN Foundation, IIT (ISM) Dhanbad, has signed an MoU with GIREDMET State Research and Design Institute of Rare Metal Industry, Russia, to collaborate on rare earth processing, critical minerals, advanced materials, and translational research across the mining value chain. The partnership will also focus on hydrometallurgical recycling technologies for lithium-ion batteries to recover valuable metals.
IEC-based technical specifications needed for second-life PV module market
The latest report from the International Energy Agency’s Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme says second-life PV modules have the potential to reduce waste and extend the value of solar assets, but their market today remains underdeveloped and requires advances in technical qualifications, scalable reuse infrastructure and supportive policy frameworks.
Epic Energy selects REFNIC as technical partner for lithium-ion battery recycling and second-life facility
Epic Energy has selected REFNIC as the technical partner for setting up a lithium-ion battery shredding facility with an installed capacity of 500 kilograms per hour of black-mass production, and a second-life battery assembly plant with an installed processing capacity of approximately 10 MWh per month.
Pre-Budget 2026: Solar and storage industry calls for tax reforms, PLI expansion, and circular economy push
Ahead of the presentation of the Union Budget 2026–27, stakeholders across India’s solar and energy storage ecosystem have urged the government to focus on tax reforms, expansion of production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes with targeted allocations, faster viability gap funding (VGF) disbursements, additional funding for residential rooftop solar, improved access to long-term and affordable green finance, and a stronger push for circular economy initiatives and grid modernisation.
Why rare earth and advanced materials are critical to India’s next manufacturing leap
Every additional EV, wind turbine, transmission line, or storage system intensifies pressure on supply chains that are already concentrated and geopolitically sensitive. Competing solely on mining is neither sufficient nor sustainable.
New process achieves 97% silver recovery from end-of-life solar panels
Australian researchers have developed a new separation technique that employs the same crushing and flotation principles used in mineral processing to recover more than 97% of silver from end-of-life solar panels.
India introduces ‘Battery Aadhaar’ system to track EV batteries across lifecycle
India’s Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has released draft guidelines for the implementation of a Battery Pack Aadhaar system—an indigenous digital identification and data storage mechanism designed to ensure end-to-end lifecycle traceability of batteries, particularly those used in electric vehicles (EVs).
Attero announces INR 150 crore investment to expand e-waste and copper recycling capacity across India
Once the new plants are commissioned, Attero’s overall processing capacity across e-waste and metals recovery will reach 244,000 tonnes per annum.
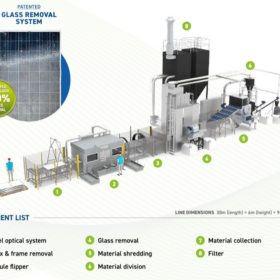
Jakson to set up high-tech solar PV module recycling line in partnership with Europe’s Ecoprogetti
Jakson Engineers Ltd will set up a high-tech solar PV module recycling plant capable of recycling around 5,00,000 PV modules, or approximately 13,500 tonnes of modules per year, recovering critical materials and enabling responsible end-of-life solar management. The recycling line will be supplied by Ecoprogetti.