Hydrogen to play limited role in building energy supply
How much hydrogen is actually needed? Several German research institutes have examined 40 energy scenarios for hydrogen ramp-up and found that 15 million GWh of hydrogen will be needed worldwide by 2050.
KKR, Hero Group to invest $450 million in Hero Future Energies
The investment will support Hero Future Energies in expanding its renewable energy capacity and capabilities across the solar, wind, battery storage, and green hydrogen technologies.
India’s electrolyzer manufacturing capacity will reach 8 GW per year by 2025, says Rystad
India will have six hydrogen electrolyzer gigafactories operational by 2025, aggregating to a combined annual capacity of over 8 GW.
Canadian pension fund invests in Mahindra’s renewables arm
Mahindra Group has agreed to sell a 30% equity stake in Mahindra Susten to the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan for around $300 million. The two parties have also agreed to set up an infrastructure investment trust so Mahindra Susten can strengthen its solar, hybrid energy, and integrated storage businesses, as well as its round-the-clock green energy plants.
Servotech launches lithium battery manufacturing arm
The New Delhi-based solar and EV charger manufacturer has formed a new arm, Techbec Industries, to manufacture lithium batteries for electric vehicles (EVs) and solar energy storage applications.
Shell to install over 10,000 charging points across India by 2030
The energy major launched the first of these electric vehicle (EV) chargers for the four-wheeler and two-wheeler segments in Bengaluru today.
Battery energy storage systems as an alternative to diesel generators
A new study suggests that battery energy storage systems charged with solar are the most attractive power backup option for commercial and industrial entities in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu.
Prescinto secures deal with energy storage major in USA
Gujarat-based Prescinto, which provides software-as-a-service (SaaS) solutions for clean energy asset management, has expanded beyond wind and solar into the rapidly accelerating energy storage market and added North America to its growing international portfolio.
Flipkart to deploy 400 electric cargo vehicles for Delhi NCR
E-commerce retailer Flipkart has partnered with electric fleet operator Magenta Mobility to add 400 electric cargo vehicles to its fleet in India’s national capital region.
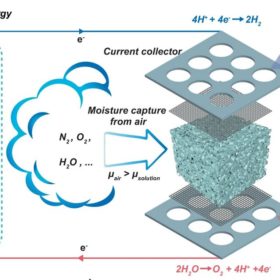
PV-powered direct air electrolysis module to produce hydrogen from moisture in air
Scientists in Australia have developed a new way to produce hydrogen using water from the atmosphere. They claim their new module can ensure stable performance and provide green hydrogen for remote areas.