Competition in intra-state transmission sector will drive India’s renewable energy progress
The intra-state transmission infrastructure is the weakest link in the grid. The introduction of competition from private players can help drive down construction costs and promote timely completion of projects, assisting the absorption of low-cost, domestic renewable energy generation.
Adani Group has the opportunity to lead India’s energy strategy
The Group’s renewable energy business (Adani Green Energy) has a market value of US$15.6 billion, which is 40% more than India’s largest thermal power generator NTPC—a company with 22 times as much capacity. The RE business is of serious global investor interest, but also materially exposed to the wider Group’s environmental, social and governance (ESG) standing. By committing to phased closure of coal plants, Adani Group could lower the risk to global capital access while aligning with the government’s vision for energy independence through fast-growing reliance on renewables.
The long read: India’s tender prices tumble, despite Discom delays
India’s state-owned electricity distribution companies (Discoms) are in dire financial straits, as they owe some $16 billion to generators, according to the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA). Despite this, national PV auctions have been oversubscribed and are setting record low tariffs in the country, indicating strong interest from developers – if the Discom challenge can be overcome.
Rooftop solar market in 2020
It has been a rocky year for installers with issues like availability of modules from Chinese suppliers, restricted construction due to local lockdowns, and uncertainty over import duties. Going forward, the market could see a dramatic rebound if net-metering is allowed with a current cap of 1 MW and re-introduced in the states that have shifted to gross-metering.
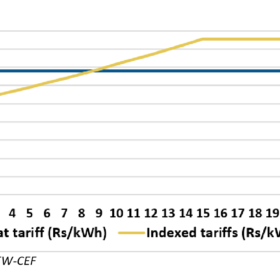
Indexed renewable energy tariffs could save discoms up to INR 21,880 crore over five years
A joint report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (Ieefa) and the CEEW-Centre for Energy Finance (CEF) has recommended indexed tariff structure over flat rate for future renewable capacity, with front-ending tariffs as low as INR 2/kWh, to ease near-term financial pressure on discoms.
India’s wind-solar hybrid capacity could grow 80 times in three years
A new report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (Ieefa) and JMK Research estimates India to have about 11.6 GW of operational wind-solar hybrid capacity by 2023.
Auctions show Indian renewables still primed for growth
A report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis says there is plenty of investment capital available for Indian renewables despite pandemic disruption.
Rajasthan could add 22.6 GW of new renewable energy capacity to the grid within a decade
The state—which has already installed an aggregate 9.6 GW of renewable energy capacity as of FY 2019-20 end—will add another 22.6 GW to the grid by the end of FY2029-30. Of the new RE addition, 18 GW will come from solar capacity.
IEEFA: Why India can’t match the Gulf region’s record-low solar tariffs
India’s solar tariffs—whilst some of the lowest in the world—are almost double the Gulf region’s US¢1.35-1.80/kWh.
Global green hydrogen project pipeline reaches 50 GW
International thinktank IEEFA says there are 50 viable green hydrogen projects under development with an estimated renewable energy capacity of 50 GW and the potential to produce 4 million tonnes of the fuel annually.