India to add more than 15 GW of renewable energy capacity annually in FY 2025 and FY 2026: India Ratings
India Ratings and Research expects India to maintain pace of renewables capacity addition owing to a significant drop in equipment prices, continued policy support, availability of liquidity, and investment plans of some of the large corporate players.
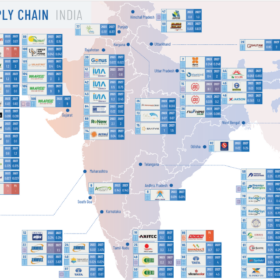
Sinovoltaics charts growth of PV manufacturing in India
The latest supply chain report from the Hong Kong-based technical compliance and quality assurance company covers India, providing information about current and planned capacity at 116 manufacturing plants.
Siemens to demerge energy business into separate listed entity
Siemens Energy India will provide solutions across the entire energy value chain – from power and heat generation, transmission to storage.
Coal share in India’s installed power capacity drops below 50%
Coal’s share (including lignite) in India’s total installed power capacity dropped below 50% in the first quarter of 2024. This is well ahead of the Government’s target to establish 50% cumulative power generation capacity from non-fossil fuel-based sources by 2030.
Navigating the future of hydrogen
Hydrogen, often lauded as a beacon of hope in the quest for a low-carbon future, stands at a pivotal crossroads. As the world grapples with the dual challenges of escalating energy demands and climate change, hydrogen presents a unique opportunity to harmonize industrial development with environmental stewardship. However, its path is fraught with complexities and obstacles that require careful navigation.
Amplus commissions third open-access solar plant in Uttar Pradesh
Amplus’ operational open-access solar capacity in Uttar Pradesh has swelled to over 200 MWp with the commissioning of the 73.4 MWp PV plant in Jhansi.
Exicom launches India’s fastest DC charger for electric vehicles
Exicom’s Harmony Gen 1.5 DC Fast charger features a modular construction enabling power outputs from 60 kW to 400 kW. The charger is suitable for in-city, highways or heavy duty fleets.
SECI extends bidding for 25 MW AC solar plant with 20 MW/50 MWh battery storage in Leh
Solar Energy Corp. of India (SECI) has extended bidding for the installation and commissioning of a 25 MW AC (50 MWp DC) solar PV plant with 20 MW/50 MWh battery storage in Leh by three weeks.
From Mumbai to Bondi
Economic cooperation between India and Australia may open doors for investment in clean energy technology but challenges still abound in a competitive global market. Vibhuti Garg and Shantanu Srivastava, of the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis, discuss the role that public funding and resource pooling could play in supporting manufacturing ambitions.
The Hydrogen Stream: Larsen & Toubro to commission electrolyzer factory this fiscal
Larsen & Toubro’s electrolyzer factory in Hazira, Gujarat, will produce electrolyzers in sizes up to 4 MW.