Coal share in India’s installed power capacity drops below 50%
Coal’s share (including lignite) in India’s total installed power capacity dropped below 50% in the first quarter of 2024. This is well ahead of the Government’s target to establish 50% cumulative power generation capacity from non-fossil fuel-based sources by 2030.
From Mumbai to Bondi
Economic cooperation between India and Australia may open doors for investment in clean energy technology but challenges still abound in a competitive global market. Vibhuti Garg and Shantanu Srivastava, of the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis, discuss the role that public funding and resource pooling could play in supporting manufacturing ambitions.
Buildings can offer gigawatts of new peak capacity as ‘batteries’
Modeling shows that shifting just one-third of the electricity consumption of commercial and institutional buildings in Australia to the middle of the day, coinciding with peak solar supply, would create almost 12 GW of new peak capacity in the National Electricity Market.
China’s clean tech dominance threatens global market stability
The influx of affordable Chinese green products is pressuring local industries in major economies, particularly the U.S. and Europe, driving down prices and potentially stifling domestic innovation due to competitive disadvantages.
Tata Power reports record profit of INR 4,280 crore for FY 2024
Tata Power has recorded INR 61,542 crore of revenue and INR 4,280 crore net profit for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024.
Malaysian government launches incentive scheme for residential solar
The Ministry of Energy Transition and Water Transformation in Malaysia is teaming up with private and public partners in the country to offer citizens financial incentives and discounts when adopting solar. It follows a government rebate scheme introduced in April.
Waaree Energies partners Ecofy for low-cost finance to rooftop solar customers
Waaree Energies Ltd, India’s largest solar PV module manufacturer, has partnered with Ecofy, a non-banking finance company backed by Eversource Capital, to provide low-cost, hassle-free finance to homeowners and MSMEs adopting rooftop solar systems.
Designing the best-performing hybrid renewable energy system for off-grid, rural communities in India
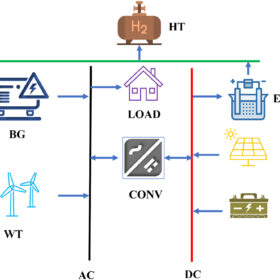
A new study evaluates seven different configurations of hybrid renewable energy systems to meet the electricity requirements of an off-grid village community in the Jaisalmer district of Rajasthan, cost-effectively and sustainably. It finds the system combining solar PV panels, wind turbines, biogas generator, lithium-ion battery, converter, electrolyser, and hydrogen tank to be the best performing as it has the lowest fuel consumption rate, net present cost, levelised cost of energy, and cost of hydrogen.
REC gets RBI nod to set up subsidiary in GIFT City, Gujarat
The proposed REC subsidiary at GIFT City will engage in lending, investment, and other financial services, contributing to the growth of India’s energy sector.
India installed 15 GW of solar capacity in FY 2024: CEEW-CEF
India added 18.5 GW of renewable energy generation capacity in FY 2024, comprising 81% (15 GW) from solar (grid-scale and rooftop).