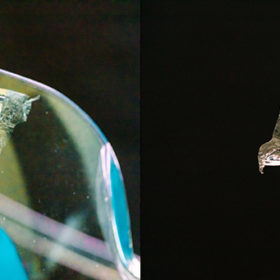Hard carbon for a high-energy sodium battery
Scientists in Japan demonstrated a hard-carbon electrode that can greatly increase the capacity of a sodium-ion battery. With further work on the long-term performance, the discovery could make sodium-ion batteries better able to compete on energy density with their lithium-ion counterparts.
The long read: Bigger yes, but better…?
It is now a well-established trend. After the switch to larger wafer sizes played out in 2019, this year has seen virtually all of the biggest PV manufacturers introduce new modules in dimensions above the 2-meter mark, and with power ratings in excess of 500 W – in some cases, as high as 800 W. As these modules begin to roll off production lines in larger quantities, it’s vital to take a look at the challenges and opportunities they bring to system design, installation, and long-term operation.
Evaluating tandem cells, from the bottom up
Scientists in Germany evaluated multiple silicon cell concepts based on both cost and efficiency in serving as the bottom layer in a perovskite-silicon tandem cell. The study, based on both simulation and experimental work, outlines advantages to various approaches with the silicon cell and concludes that in almost every case, perovskite-silicon tandem cells have the potential to bring solar costs down below what could be achieved with silicon alone.
PV powered desalination is “the most competitive design”
Scientists in France conducted an analysis on the competitiveness of water desalination, taking a large scale project planned for Morocco as a case study. The research concludes that PV without storage is the cheapest option to power desalinators, and will likely remain so until at least 2030.
The long read: The cracks are showing
Finding tiny cracks in a silicon solar cell is not that easy, particularly given that these cracks initially have little or no effect on module performance. But a number of common occurrences in a module’s lifetime can cause cracks to grow, rendering whole areas of a cell useless. And this is increasingly being recognized as one of the most significant risks to module reliability – one which the PV industry is hard at work to mitigate.
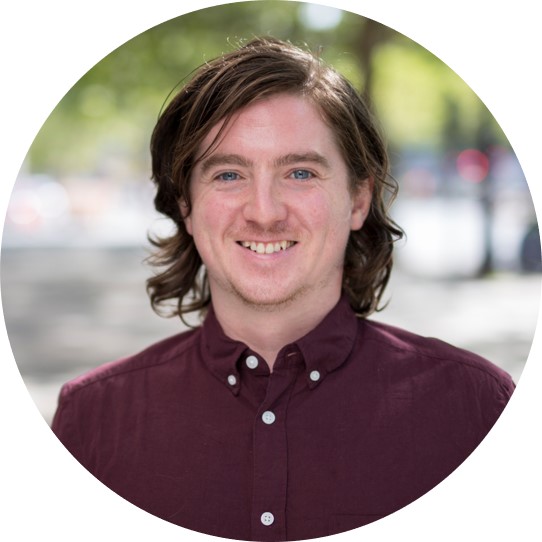
A solar cell so thin, it can rest on a soap bubble
Scientists at Saudia Arabia’s King Abdullah University of Science and Technology demonstrated an organic PV cell that can simply be printed onto a piece of paper. The cell set a new efficiency record for a fully inkjet-printed device, and its designers envisage applications in integrated medical sensors.
The long read: The state of solid-state batteries
Solid-state batteries hold the potential to overcome many of the limitations of today’s lithium-ion storage technologies. Though they have been a research topic for more than 30 years, and more recently have seen billions of dollars poured into their development by leading carmakers and electronics giants, commercial development is still extremely limited. Major roadblocks remain in the way of both device performance and industrial-scale processing. pv magazine recently caught up with solid-state’s research community for a look at where the technology stands.
‘Spontaneous de-doping’ for 17.8%-efficient perovskite mini-module
U.S. scientists have found a new ‘de-doping’ process in perovskite solar cells that could cut production costs and produce better devices. They have used this to fabricate a mini-module with 17.8% efficiency.
IIT researchers consider fate of end-of-life solar modules
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Technology in New Delhi have taken a close look at the potential impact of growing volumes of PV waste and conducted surveys which suggest a lot more work is needed from manufacturers and policymakers to develop management systems for end-of-life PV products.
Microsoft trials hydrogen-powered data centers
The software giant has begun testing hydrogen fuel cells as a back-up power source at one of its U.S. data centers. A 250 kW pilot system successfully powered part of the facility for 48 hours and the company is now eyeing 3 MW systems to replace back-up diesel generators.