India Ratings and Research (Ind-Ra) has maintained a neutral outlook for India’s power sector for FY27, citing steady long-term electricity demand growth of 5.5%–6.0% year-on-year.
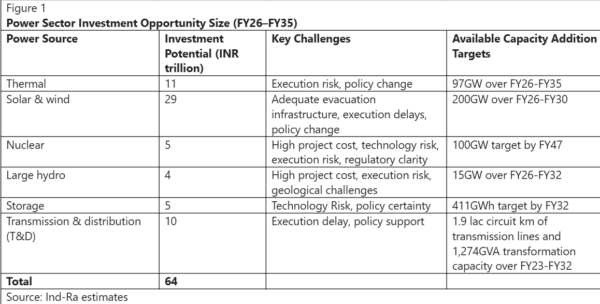
The agency estimates a massive investment opportunity of around INR 64 trillion in the power sector (including INR 29 trillion alone in solar and wind and INR 5 trillion in energy storage) over FY26–FY35, supported by favourable policy frameworks, large corporate capex plans and rising foreign investments. However, managing the execution, technology, and funding risks remains a key monitorable.
Renewables to dominate capacity addition
Ind-Ra expects renewable energy to continue to dominate incremental capacity additions, with 40 GW in FY26 and 35 GW in FY27, though the pace of additions may moderate primarily due to transmission constraints, slower tendering, and unsigned power purchase agreements.
In FY26, 34.7 GW has already been added by end-December 2025, driven by benign equipment rates, interstate transmission system charges waiver expiry, favourable regulatory policies, and a lower capital cost.
“Renewable energy will continue to dominate incremental capacity additions, although the pace may moderate in FY27 due to slower tendering and transmission constraints,” says Pritha Preshi Sharma, Associate Director, Corporate Ratings, Ind-Ra.
However, “energy transition will hinge on rapid development of storage and/or round-the-clock sizing of renewable projects and adequate transmission infrastructure.”
The National Electricity Plan projects storage requirements of 82.37 GWh by FY27 and 411.4 GWh by FY32, split between pumped storage (PSP) and battery energy storage systems (BESS). Falling battery prices have made BESS more viable. While PSP offers a longer life and stable discharge, gestation timelines and higher landed conversion charges shall play a role in its adoption. Transmission expansion is equally critical, with 1,91,474 circuit km planned between FY23-FY32.
Thermal power to remain the backbone of electricity generation
Ind-Ra expects coal‑based thermal power to remain the backbone of electricity generation, contributing around 70% of the total generation in FY26–FY27, despite its installed capacity share declining below 50% (246.9 GW of 513.7 GW as of Dec. 2025).
Thermal plant capacity utilisation is anticipated to remain healthy at around 65% over FY26-FY27, supported by the base load demand, even as renewable energy gain prominence, and steady power demand growth.
Ind-Ra expects 10 GW of thermal capacity commissioning in FY 26 and 5 GW in FY27.
Evolving manufacturing ecosystem
Solar module manufacturing capacity has reached 144 GW and cell capacity at 27 GW by end-December 2025, driven by favourable policies like Approved List of Models and Manufacturers (ALMM), Production-linked Incentive schemes, and levy of duties on imports. The likely implementation of ALMM-2 (for solar cells) has also been driving most large-to-mid scale players towards backward integration for cell lines.
However, Ind-Ra believes an oversupply of module capacity, fresh debt-funded capex for cell lines, and limited export potential amid US tariffs may pose challenges, particularly for small players and could lead to industry consolidation.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.