India’s power sector is undergoing a transformative shift in response to new global realities. As international supply chains are being redefined due to trade disputes, pandemic-era disruptions, and increasing calls for energy security, India is adapting its infrastructure and strategy to align with emerging global dynamics.
This shift is not only about meeting the country’s growing energy demand but also about enhancing domestic manufacturing, reducing import dependence, and integrating cleaner, smarter power technologies. The evolution of India’s power infrastructure today reflects both a local response to global pressures and a long-term national vision of sustainability and resilience.
With renewable capacity expanding, grid upgrades underway, and policies fostering local supply chains, India is navigating a complex but promising energy transition.
Shifting Global Supply Chains and Their Impact on Power Infrastructure
The reconfiguration of global supply chains is one of the most influential trends shaping India’s power sector. Over the past few years, geopolitical frictions, including the US-China trade tensions and regional conflicts, have exposed the vulnerabilities of over-reliance on imported energy components. These include solar cells, inverters, transformers, and battery materials, much of which have traditionally been sourced from China.
India has responded by initiating efforts to reduce its import dependency and build self-sufficiency in energy infrastructure manufacturing. Domestic industries are now being encouraged to produce solar photovoltaic modules, lithium-ion batteries, and rare-earth elements used in wind turbines. For example, India possesses rare-earth reserves but has long lacked processing capacity. A government-backed initiative is now working to bridge this gap through public-private partnerships.
Additionally, the shift in supply chains has created an opportunity for India to position itself as an alternative global manufacturing hub. Global energy companies are exploring partnerships and manufacturing setups in India, attracted by its low labor costs, policy incentives, and expanding energy market. This reorientation is gradually shaping a more resilient, localized, and globally integrated Indian energy sector.
Expansion of Renewable Energy and Transmission Upgrades
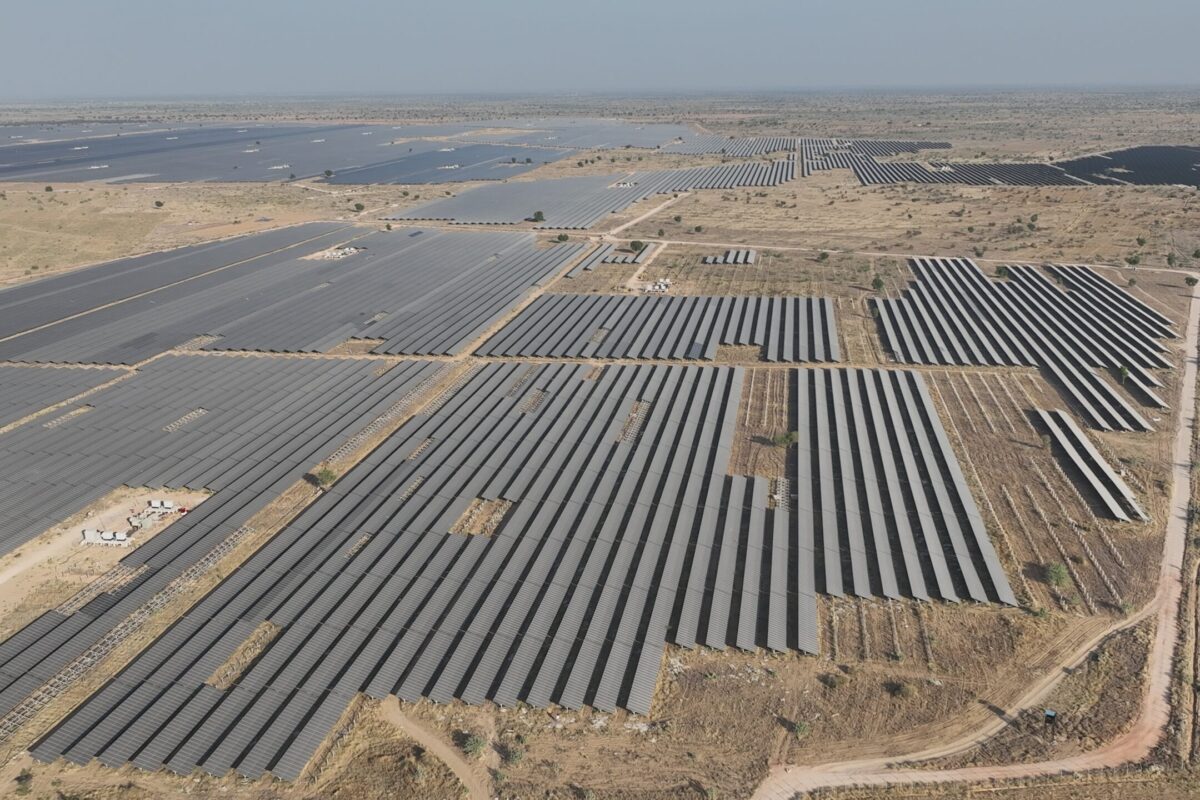
India’s power generation mix is steadily shifting towards renewables, supported by strong policy frameworks and ambitious national targets. As of early 2025, non-fossil sources account for nearly half of India’s total installed power capacity, which exceeds 468 gigawatts. Solar and wind power are leading this growth, with large-scale projects like the Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan and the hybrid energy park in Gujarat serving as high-impact examples.
However, adding capacity is only one part of the challenge. Transmission and distribution networks must evolve to handle variable renewable generation and connect energy-rich regions with demand centers. Historically, inadequate transmission infrastructure has led to bottlenecks and underutilization of available generation. To address this, India is expanding high-voltage transmission lines and investing in flexible grid technologies.
Power Grid Corporation of India, the central transmission utility, has undertaken major projects to install 765 kV substations and modernize grid connectivity. In parallel, digital innovations are gaining traction. The “India Energy Stack” is a government initiative aiming to create an integrated digital layer for energy data, allowing utilities to track demand, manage loads, and forecast requirements with greater precision.
These developments signal a transition from merely expanding power generation to building a responsive, intelligent grid that can support both base-load stability and renewable variability.
Building Domestic Capabilities Through Policy and Investment
The shift toward energy independence requires more than just infrastructure; it calls for a strong domestic manufacturing ecosystem. Recognizing this, India has launched targeted programs to scale up production of key components for the renewable sector. The Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme, for instance, is fueling investments in solar module manufacturing, advanced battery storage, and green hydrogen technologies.
In states like Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, and Andhra Pradesh, energy-focused industrial zones are being developed to support this manufacturing push. Companies are setting up gigafactories to produce batteries and solar panels, while R&D in clean energy technologies is being fostered through academic and industrial collaboration.
However, challenges remain. The cost competitiveness of Indian manufacturing is still evolving. Chinese imports often remain cheaper due to economies of scale and integrated supply chains. To counter this, India will need to invest in automation, materials innovation, and process efficiency. Financing is another hurdle, particularly for small and mid-sized firms aiming to enter energy manufacturing.
Despite these challenges, the strategic intent is clear. India’s energy policies are no longer just about generating electricity. They are about securing strategic inputs, localizing innovation, and building capabilities that align with a larger industrial and environmental vision.
Toward a Resilient and Digitally Enabled Power Future
As India moves forward, the focus is gradually shifting toward resilience and flexibility. The goal is not only to meet current energy demands but to build a power system capable of withstanding global shocks, supporting economic growth, and enabling long-term sustainability.
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are emerging as key components of this future. These systems allow renewable energy to be stored and used during peak demand hours, reducing reliance on coal-based peaker plants. While still at an early stage in India, pilot projects and large-scale tenders are paving the way for wider adoption.
Grid modernization is another essential element. Smart meters, AI-based forecasting, and digital twins of energy infrastructure are being introduced to improve grid visibility and efficiency. With growing urbanization and electrification of transport, especially through electric vehicles, the grid will need to be more agile and responsive.
India is also looking beyond its borders. Cross-border energy cooperation is gaining momentum through initiatives like the One Sun One World One Grid project, which aims to connect countries across South Asia and beyond through a unified renewable energy grid. These efforts reflect India’s ambition not only to secure domestic power needs but also to play a leadership role in the global energy transition.
Conclusion
India’s power infrastructure is evolving at a critical moment in global energy and trade history. As supply chains shift and the world seeks more sustainable energy systems, India is leveraging this opportunity to strengthen its domestic manufacturing, expand renewables, modernize the grid, and reduce strategic vulnerabilities. While the journey is complex and layered with challenges, from financial constraints to technological gaps, the direction is clear. India is no longer just a large energy consumer. It is becoming a builder, innovator, and exporter of power solutions tailored to a changing world. The success of this transition will depend on consistent policy implementation, private sector participation, and global cooperation. If achieved, India’s energy transformation could serve as a model for other emerging economies navigating similar transitions in an increasingly interconnected world.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.






By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.