Norway’s Statkraft, Aker Horizons partner to explore green hydrogen and ammonia production in India
Norwegian renewable energy developer Statkraft has partnered Norway’s green investment company Aker Horizons to explore fully-integrated renewable power generation and green hydrogen production in India, targeting local steel and fertilizer industries.
Mobile agrivoltaic system from the Netherlands
Created by a Dutch group of companies and research institutions, the mobile solar system may also be combined with an electrolyzer for hydrogen generation. Two prototypes are currently being tested by a farmer and a research institute in the Netherlands.
Growatt unveils solar rechargeable portable power station
Chinese inverter maker Growatt has launched Infinity 1500, a portable power station for off-grid applications.
Linde raises 26% stake in 32.5 MW solar plant for self-consumption
The captive solar plant is developed by Avaada Group through a special purpose vehicle called Avaada MHYavat. The solar electricity generated will power energy-intensive air-separation operations of the industrial gas producer.
Larsen & Toubro, IIT Bombay partner on green hydrogen technology development
The Indian multinational EPC solutions provider has signed an agreement with the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay to develop scalable and cost-effective solutions for green hydrogen production jointly.
Polysilicon maker predicts 5-year shortage of solar raw material
TBEA-owned Xinte Energy says it cannot produce polysilicon quickly enough to meet demand and wants shareholders to back its bid to quadruple its manufacturing capacity by mid 2024.
Borosil Renewables to acquire Europe’s largest solar glass maker Interfloat Group
With this acquisition, the Indian manufacturer’s solar glass output will grow to 750 tonnes per day (TPD) from the current 450 TPD.
Torrent Power acquires 50 MW solar plant from Canadian developer SkyPower
The solar plant, located in Telangana, benefits from a 25-year power purchase agreement (PPA) with the State discom at a fixed tariff of approx. INR 5.35/kWh. It has a remaining useful life of approx. 20 years.
India calls for credit guarantee fund to drive solar adoption in electricity-deprived regions globally
RK Singh, India’s power minister, and president of the International Solar Alliance (ISA) Assembly, called on nations to support solar investments in developing and under-developed regions, including Africa, through low-cost finance and credit guarantee fund.
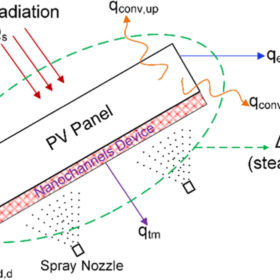
New solar module cooling tech based on porous nanochannels
US scientists have utilized a nanochannels device to cool down the operating temperature of a commercial PV module and have found that the proposed technique is able to improve power yield by up to 32.8%. Spray droplets are dispersed over the nanochannels device in order to eliminate the need for a continuous supply of a coolant.