The effects of solar module elevation on ground-mounted PV
Scientists in Hungary found that ground-mounted PV modules at an intermediate elevation of 1.1 m achieve the highest efficiency and power output due to improved airflow and reduced cell temperature. Their study also estimated a levelized cost of electricity of $0.0843/kWh and 577.78 kg CO₂ mitigation over 25 years, while noting results are specific to concrete surfaces.
The real question for India: Should we chase the next technology or optimize global best practices?
By combining proven global practices with solutions designed for Indian conditions, offering choices for different customer needs, and continuing to invest in meaningful innovation, India can build a solar ecosystem that is resilient and inclusive.
Avaada Group partners with GRIDCO, IIT-Bhubaneswar to set up green hydrogen Centre of Excellence in Odisha
Avaada Group has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with GRIDCO and IIT-Bhubaneswar to establish a state-of-the-art Centre of Excellence (CoE) in Odisha focused on integrated research, innovation, and technology development in green hydrogen.
Fraunhofer ISE achieves 30.6% efficiency for perovskite-silicon tandem based on industry-standard bottom TOPCon cell
Researchers at Fraunhofer ISE have developed a perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell using a TOPCon bottom cell with standard textured front surfaces. Their results show that TOPCon bottom cells can perform comparably to heterojunction cells in tandem devices in terms of shunt resistivity, supporting scalable, cost-effective industrial production.
World’s first solar park featuring hydrogen-producing PV modules takes shape in Belgium
A 2 MW solar park in Wallonia, Belgium, will rely 50 kW of hydrogen-producing solar modules developed by Solhyd, a spin-off from KU Lueven. The installation will be the first demonstration of Solhyd’s technology at a commercially-relevant scale.
Musk proposes PV-powered AI satellite network to fight global warming
Elon Musk says a constellation of solar-powered artificial intelligence satellites could regulate the planet’s energy balance and limit global warming.
Rethinking transformer design for the energy transition
With renewables’ share in power generation expected to grow significantly, there will also be a push in the demand for next-generation transformers that are capable of handling the intermittent nature of solar, wind, and other non-polluting sources of energy. The grid of the future demands not only more transformers but smarter, adaptive, and sustainable designs that can support India’s ambitious renewable targets and fast-rising power demand.
Solex Energy partners Germany’s ISC Konstanz, unveils rear-contact solar module concept
Solex Energy Ltd has partnered with Germany’s ISC Konstanz to upgrade its upcoming TOPCon cell line and adopt next-generation rear-contact and c-Si tandem/perovskite solar technologies. The manufacturer also unveiled its concept rear-contact solar module, which is set to enter commercial production by FY 2027.
KAUST explores polymer alternatives to glass for solar panel covers
Researchers at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have published a review that looks at polycarbonate sheets as an alternative to solar cover glass. Their findings indicate that this new materials have a combination of low weight, mechanical strength, optical transparency, and thermal resistance that is worthy of further investigation.
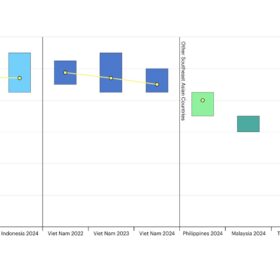
IEA says cost of capital for solar remains high in Southeast Asia
The International Energy Agency (IEA) says the cost of capital for solar remains higher in Southeast Asian countries than it does in other emerging and developing economies.