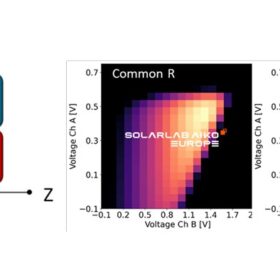
Aiko achieves 34.76% efficiency for 2-terminal perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell
The Chinese manufacturer said its 2-terminal 34.76%-efficient perovskite-silicon tandem lab-scale cell is based on heterojunction technology and developed by a collaboration of Solarlab Aiko Europe, Aiko headquarters, and its R&D in Yuwi, China.
The Hydrogen Stream: IIT Kanpur, HBTU to jointly establish Centre of Excellence for Green Hydrogen in Uttar Pradesh
The Centre of Excellence, operated from the campus of IIT Kanpur and HBTU Kanpur, will prioritize research and development focused on green hydrogen production, storage, transportation, safety standards, testing, demonstrations, and industrial use. Special emphasis will be on applied research and technological solutions for industries such as refineries, fertilizers, transportation, manufacturing, and energy systems.
The future of impact funding: Aligning capital with sustainable outcomes
The largest area of green financing is energy-efficient machinery, which supports MSMEs in modernising production lines and reducing operational energy consumption. Significant capital is also being channelled into rooftop solar installations, electric vehicles, and enterprises operating in the water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH) sectors, across clusters such as manufacturing, healthcare, and food processing.
Solex Energy partners with Malaysia’s TT Vision on solar manufacturing automation and talent development
Solex Energy Ltd has signed a non-binding Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Malaysia-based automation technology company TT Vision Holdings Berhad to collaborate on advancing solar manufacturing automation, engineering excellence, and talent development in India.
MIT-WPU researchers develop safer liquid hydrogen transport system
Researchers at India’s MIT World Peace University (MIT-WPU) have developed a Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier (LOHC) system capable of transporting hydrogen in a stable liquid form that is non-flammable, non-explosive, and manageable at normal temperatures and pressures. This breakthrough removes one of the biggest barriers slowing the widespread adoption of hydrogen in India.
Smart Joules raises $10 million in Series B funding from Neev II Fund, Waaree Renewable Technologies, and Spectrum Impact
Smart Joules will use the proceeds to expand its energy-efficiency and cooling operations into newer sectors and larger-scale projects, including manufacturing, building automation, and district cooling, while further strengthening the company’s technology, analytics, and on-ground execution capabilities.
From waste to wealth: Circular strategies driving a sustainable India
The promise of India’s circular economy lies in its ability to turn environmental challenges into engines of growth. Achieving it will take investment, innovation, and clear ways to measure progress.
Keeping the smart grid cyber secure
As smart grid tech is rolled out around the world to modernize legacy assets and integrate renewable energy generation, it is also making the electricity network more prone to cyber attacks. IEC Standards provide protection but they also are challenged to keep up with the latest threats.
Avaada Group partners with GRIDCO, IIT-Bhubaneswar to set up green hydrogen Centre of Excellence in Odisha
Avaada Group has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with GRIDCO and IIT-Bhubaneswar to establish a state-of-the-art Centre of Excellence (CoE) in Odisha focused on integrated research, innovation, and technology development in green hydrogen.
India’s green hydrogen future needs demand to keep pace with ambition
If India solves demand creation intelligently, it can become a global price-setter, not just another participant in the hydrogen economy.