Pre-Budget 2026: Solar and storage industry calls for tax reforms, PLI expansion, and circular economy push
Ahead of the presentation of the Union Budget 2026–27, stakeholders across India’s solar and energy storage ecosystem have urged the government to focus on tax reforms, expansion of production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes with targeted allocations, faster viability gap funding (VGF) disbursements, additional funding for residential rooftop solar, improved access to long-term and affordable green finance, and a stronger push for circular economy initiatives and grid modernisation.
Building responsibly: India’s steel sector and the carbon budget challenge
India’s steel sector stands at a decisive moment. As the country pursues industrial growth, it must also demonstrate that development and decarbonisation can move together. The carbon budget framework offers not a constraint, but a compass, guiding industry toward innovation, resilience and global competitiveness.
India’s transition to green steel is expected to be gradual, driven by renewables in the near term: ICRA
ICRA expects the Indian steel industry’s decarbonization to be gradual, with near-term emission reductions driven mainly by higher adoption of renewable energy and improvements in operational efficiency, as high costs and technology constraints limit faster decarbonization.
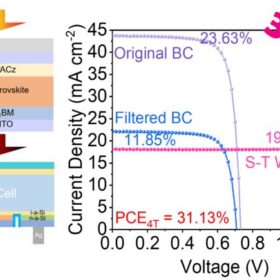
Chinese scientists build 31.13%-efficient perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell via 2D seeding agent
Researchers in China developed a novel two dimensional (2D) seeding agent to regulate crystallization in a 1.80-eV wide-bandgap perovskite film. A perovskite-silicon tandem device made with the resulting optimized subcell achieved an efficiency of 31.13%, outperforming a control device.
New Delhi to host Bharat Electricity Summit 2026 from 19–22 March
The four-day Summit will focus on the entire power value chain, including power generation (with emphasis on clean energy systems such as solar, wind, hydro, green hydrogen, etc.), transmission and distribution, energy storage, and energy efficiency solutions.
Smart grids, smarter solar: Preparing India’s grid for high renewable penetration
Smart grids represent a fundamental shift in how electricity networks are planned and operated. By leveraging digital technologies, real-time communication, and automation, smart grids enable utilities to respond dynamically to changing grid conditions. For India, this transformation is critical to maintaining reliability while integrating large volumes of solar and wind power.
Grid-forming inverters significantly enhance grid stability, national lab finds
The Kauaʻi Island Utility Cooperative in Hawaii, which deployed storage before grid-forming inverters became available, became a test case for diagnosing grid issues that can arise with older grid-following inverters, and how grid-forming inverters can stabilize a grid.
Uniper, AM Green sign long-term offtake agreement for up to 500,000 tons per year of renewable ammonia from India
Uniper has signed the agreement to offtake up to 500,000 tons per year from AM Green’s green ammonia projects. The first shipment is expected to happen as early as 2028 from AM Green Ammonia’s first 1 million ton per annum (MTPA) under construction plant in Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh.
India’s smart metering boom: How decentralized IoT is reinventing the power grid
The Indian power system is evolving faster than most global peers. Electricity demand is rising. Rooftop solar, electric mobility, and distributed generation are accelerating. The grid, once designed for predictable one-direction flows, is becoming a dynamic, decentralised organism. To manage it, India requires data that is just as distributed as the energy sources feeding the system. This is where decentralised RF mesh networks have begun to play an important role.
The real question for India: Should we chase the next technology or optimize global best practices?
By combining proven global practices with solutions designed for Indian conditions, offering choices for different customer needs, and continuing to invest in meaningful innovation, India can build a solar ecosystem that is resilient and inclusive.