Hydrogen: The steel industry’s next big step toward decarbonization
Given that global steel demand is projected to grow by 32% by 2050, largely driven by infrastructure expansion and industrial development, the need to decouple steel production from carbon emissions is both urgent and complex. Here is where hydrogen, particularly green hydrogen, emerges as a powerful catalyst for change.
Surplus solar panels offer timely solution for industry under pressure
Supply chain challenges, subsidies and tariff uncertainties are forcing the solar energy industry to find significant cost efficiencies. As older models of installed solar panels become harder to source, the growing second-life solar market helps industry find replacement panels and other equipment.
UK parliament calls for solar supply chain law, forced labor import ban
Cross-party human rights committee says legislation needed to combat forced labor in solar supply chains, in report urging the UK government to introduce mandatory due diligence measures. Solar Energy UK expresses disappointment in committee’s portrayal of the UK solar industry.
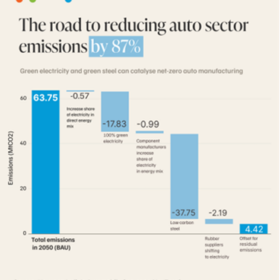
India’s auto industry can cut emissions by 87% through green electricity, low-carbon steel: CEEW
India’s automobile industry can cut its manufacturing emissions by up to 87% by 2050 with a shift to 100% renewable energy, green steel, and partnerships with suppliers to cut emissions, finds a new study by the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW).
US launches national security probe into polysilicon imports
The US Department of Commerce (DoC) says it will investigate the potential for export restrictions by foreign countries, as well as their ability to “weaponize” their control over supplies of polysilicon.
US-China tariff negotiations and impacts
Although the suspension of the 24% tariff under Section 301 sends a signal of easing, the retention of the full 10% under Section 201 and the average 83% anti-dumping/countervailing duties means that Chinese solar PV exports to the US still face a combined tax rate of nearly 200%.
The opportunity for Indian solar firms amid U.S.-China tariff war
While the tariff war between the U.S. and China presents challenges to global trade stability, it also opens up opportunities for Indian solar firms. Through strategic alignment, domestic policy support, and favorable international positioning, India stands to strengthen its role in the global clean energy supply chain.
U.S. Commerce Department slaps unexpectedly high tariffs on solar imports
Coalition trade lawyer says the U.S. Department of Commerce’s final tariffs on solar cells and modules from Cambodia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam are among the highest rates he’s ever seen.
Myanmar earthquake disrupts solar wafer production, global supply chain
The recent 7.7-magnitude earthquake in Myanmar has disrupted solar wafer production in western China, where about 50% of the country’s wafer capacity is concentrated. Major manufacturers have suspended operations due to equipment failures, raising concerns over supply shortages and higher global solar prices.
Indian heavy industries present 20 GW open access solar opportunity
A new report by Ember finds that steel, cement, and aluminium industries can profitably integrate 20 GW of solar power to run their operations.