Minister outlines plan to become global renewables leader, at Intersolar Europe
Underlining India’s commitment to becoming the global renewable energy leader, Shri Anand Kumar, secretary of the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, said the country plans 500 GW of capacity by 2030. He also underlined plans to become a solar and storage manufacturing hub; and said the International Solar Alliance needs to widen its membership.
Is national 225GW renewables target achievable?
There was incredulity in some quarters as the federal government raised its renewables ambition another 22%, but the stellar performance of the past four years points to the new target being a realizable one.
Falling battery costs to push solar, wind to 50% electricity generation by 2050, but electricity still failing CO₂ reduction targets – BNEF
Solar PV capacity is set to grow 17-fold, and wind six-fold, by 2050, to account for nearly half of global electricity generation, predicts BNEF, while investments will reach US$11.5 trillion. Cost reductions will drive this charge, particularly in the battery market, which will benefit from the EV manufacturing ramp up. Despite this, the electricity sector is still failing to bring CO₂ emissions down to the required levels, with its continued dependence on gas.
Global PV market to grow by another 621.7 GW by 2022, SolarPower Europe says
Global newly installed capacity for 2018 is forecast to reach 102.6 GW, of which “only” 39 GW are expected to come from China. Fourteen countries are expected to cross the GW threshold this year.
New solar benchmark costs announced for off-grid, rooftop
India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has announced the new benchmark costs for off-grid solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and rooftop solar projects for the financial year (FY) 2018-19.
Is SoftBank’s $100 billion investment in Indian solar realistic?
While news of Japan’s SoftBank announcing up to USD 60-100 billion investment in India’s solar PV power generation is creating ripples across the industry circles, industry analysts feel that the committment sounds unrealistic in view of India’s current PV market status and future needs.
2018 global PV market to see negative growth following China backtrack
Global solar PV demand this year will be less than in 2017, on the back of China’s latest policy decision, says TrendForce. Overall, it sees new installs dropping 40% in China to 31.6 GW. The protectionist measures taken by the U.S. will also be weakened by the resulting falling module prices.
BHEL wins INR 1.25 billion worth of solar PV plant orders in Gujarat
The first order for installing a 20 MW PV power plant has been placed by Gujarat Alkalies and Chemicals Limited (GACL), while the other, for a 10 MW PV power plant, has been received from the Gujarat State Fertilizers and Chemicals Limited (GSFC). Both of the solar PV power plants will be installed at the Gujarat Solar Park in Charanka, Gujarat.
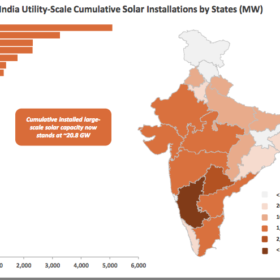
India records best ever quarter, but safeguard duties holding solar industry back – Mercom
According to Mercom India, the Indian solar PV industry has recorded its strongest quarter since the launch of the National Solar Mission. In addition to declining module prices, both rooftop and utility-scale installations saw strong growth. Clarity is needed, however, on the ongoing safeguard duty saga, to drive the industry forward.
India to launch its own battery cell production
India’s PV sector is expanding at a serious pace, creating jobs and further securing energy supply for many businesses. Yet, sourcing battery cell technology at the current rate resulted in annual foreign exchange of Rs. 1012 crore creating deficits, that hopefully can be averted in the future.