Double blow for SECI as mega tenders are met with apathy
Only three bidders have come forward for huge manufacturing-linked solar and solar-wind hybrid procurement exercises. The separate auctions – originally intended to drive 12.5 GW of new generation and 5 GW of manufacturing capacity – prompted figures of just 3.05 GW and 600 MW, respectively.
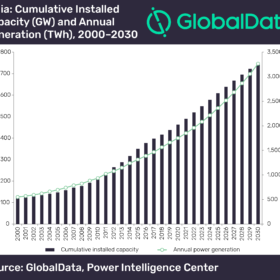
Solar leads renewables charge – but not fast enough
Latest forecasts predict capacity expansions of ever cheaper PV and wind power generation up to 2030 will do little to dethrone king coal in India.
Canadian Solar buys Suzlon’s 30 MW projects in Telangana
Suzlon Energy has sold subsidiaries Amun Solarfarms and Avighna Solarfarms to Canadian Solar for Rs545 million. The company set up the units as special purpose vehicles for two solar projects of 15 MW each, at Ramannapet and Kamareddy.
Up to $1 billion expected from Sterling & Wilson solar share sale
Around US$1 billion is expected to be raised in the sale of up to 30% of Sterling & Wilson’s solar engineering arm. The funds will come from a pre-listing stake sale followed by an initial public offering (IPO), and will be used to reduce the debt of the 153-year-old conglomerate.
Enhancing energy trading in South Asia
The Indian Ministries of External Affairs and Power, in collaboration with the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), organized the South Asia Power Summit 2018, held recently in New Delhi. The daylong conference highlighted that diversity of energy resources in South Asian countries brings the opportunity to provide affordable, low-carbon energy in the region. The business case for enhanced energy trading in the region, and challenges faced in inter-country electricity trading were important elements of this discussion.
Solar, wind cheapest source of new generation in major economies – report
Solar and/or wind are said to be the cheapest source of new energy generation in all major economies, apart from Japan, finds BloombergNEF. It adds that China’s utility-scale PV market has contracted by over a third this year; and that battery costs are set to drop a further 66% by 2030, driven by EV adoption.
NTPC tenders 1.2 GW of grid connected solar capacity
The projects, in Maharashtra, will be commissioned through a reverse auction with technical bidding to close on December 19. The deadline for the submission of financial bids and the date for the reverse auction after the opening of financial bids, will be published in due course.
Extent of India’s new utility-scale solar has almost halved in six months
India added 1.2 GW of large-scale projects in the third quarter of 2018-19, taking new capacity in the first half to 1.9 GW. The numbers are down 43% and 44%, respectively, on the same periods of the previous year, according to Bridge to India’s quarterly India Solar Compass.
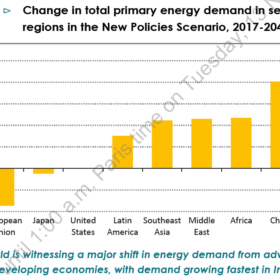
India’s energy demand will more than double by 2040 – IEA
The world is witnessing a major shift in energy demand from advanced to developing economies, with demand growing fastest in India – according to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA’s) latest World Energy Overview.
Tariff tussle grows over pricing of 970 MW project
The Solar Energy Corporation of India (SECI) and Karnataka Electricity Regulatory Commission (KERC) have locked horns over the power pricing of a 970 MW solar project.