Applications open for solar manufacturing incentives
Manufacturers can apply for incentives to set up gigawatt-scale solar factories in India. Applications can be submitted until June 30 and the list of successful recipients will be announced on July 26, with letters of award to be issued four days later.
India could have 2.95bn tons of solar waste by 2047
Researchers led by the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi have projected the waste expected from end-of-life solar panels and related components. They assumed 347.5 GW of total installed solar generation capacity would be reached this decade. The academics said the waste would include critical metals worth around $645 trillion, 70% of which could be recovered.
IEA highlights solar’s dependence on Chinese copper processing
The sheer volume of new power lines which will be required to accommodate the rising tide of solar installations ensures copper has been included by the International Energy Agency on its list of minerals which must keep flowing if the energy transition is to stay on course. And it’s not production that’s the potential bottleneck.
Adani Green transfers stake in solar manufacturing arm to Adani Enterprises
Adani Enterprises, which already controls Mundra Solar PV, has acquired a 74% stake in PV cells and modules manufacturing business Mundra Solar Energy through its subsidiary. The move will bring synergy in the company’s solar manufacturing operations and solidify its position in this space.
Maxeon launches frameless rooftop solar panels
Maxeon’s Air technology platform brings solar to previously inaccessible roof spaces.
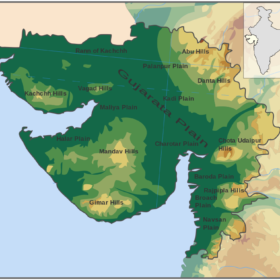
ReNew Power to set up 2 GW mono PERC solar factory in Gujarat
The vertically integrated factory, located in the Dholera Special Industrial Region, will produce 2 GW of mono PERC solar cells and modules annually. Production is expected to start from the next fiscal year.
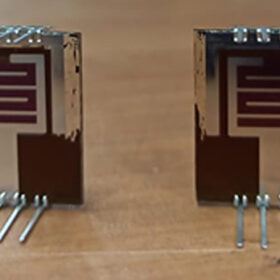
Micro III-V solar cell with 33.8% efficiency
Developed by a French-Canadian research group, the triple-junction cell is based on indium gallium phosphide (InGaP), indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) and germanium (Ge) and has an active area of only 0.089 mm2. It can be used for applications in micro-concentrator photovoltaics (CPV).
Compressed air tech for solar module cleaning, cooling shows promise in India field-testing
British scientists have reported significant restoration of the panel performance with the experimental compressed air system developed by them for the simultaneous cleaning and cooling of PV modules. The system was built with a compressed-air unit which was made of a compressor, an air tank, and an airflow regulation valve, and a series of nozzles. The technique was tested on a PV system located in northwestern India.
India launches anti-dumping probe for solar cells from China, Thailand and Vietnam
The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) under the commerce ministry stated the Indian manufacturers provided sufficient evidence to warrant the initiation of an investigation into the alleged dumping of solar cells. The investigation will aim to determine the existence, degree and effect of the dumping and recommend an amount of anti-dumping duty to offset the material injury to domestic manufacturers.
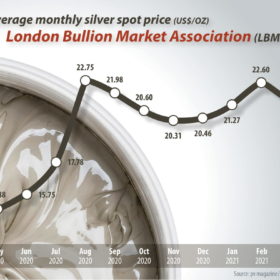
The long read: All that glitters is HJT
The devil is in the details, as they say, and when it comes to the next generation of mass-produced, high-efficiency PV cells, silver costs may be devilishly hard to reduce. Making things worse, prices for the precious metal are now heading in the wrong direction.