Reliance’ green energy giga complex will be ready for commissioning this year, Adani announces further investment in Gujarat
Reliance Industries and Adani Group, which have made big investments in creating an integrated renewable energy ecosystem in Gujarat, announced their further plans for the state at the 10th Vibrant Gujarat Global Summit.
Saatvik Solar appoints channel partner for Maharashtra and Goa region
Gurugram-based Saatvik Solar has appointed Celestial as an exclusive channel partner to market and sell its PV modules in Maharashtra and Goa.
Israeli startup launches 530 W bifacial PVT panel
P.G. Solar Greener says that its new panels have a thermal capacity of 1,280 Wh. They can reportedly achieve an overall dual electrical efficiency of 26%, due to an embedded cooling technique.
New solar tree design offers improved module cooling, lower shading losses
Researchers in Hungary have proposed to build photovoltaic trees with a significant distance between the solar panels. The proposed sunflower-shaped design reportedly reduces shading losses between the panels while improving cooling and heat dissipation.
Premier Energies secures 608 MW solar module supply contract with NTPC
Premier Energies has secured an INR 1,700-crore PV module supply contract with NTPC. It will supply 608 MW of bifacial PV modules built with made-in-India cells to NTPC’s Nokh Solar Project in Rajasthan.
Meyer Burger unveils black HJT solar panels for balcony applications
Switzerland-based manufacturer Meyer Burger has developed black heterojunction (HJT) solar modules for balconies, featuring 800 W microinverters, smart control units, and mounting systems.
Make PV modules as cheap as possible, but not cheaper
In a new monthly column for pv magazine, the International Solar Energy Society (ISES) explains how reducing glass thickness in PV modules may fracture the solar industry, impacting PV module and PV tracker suppliers, engineering, product and construction companies, and PV plant owners.
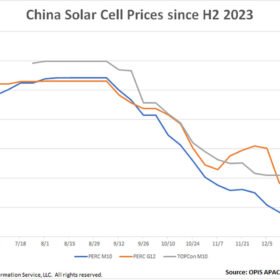
China solar cell prices decline on sluggish downstream demand
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides a quick look at the main price trends in the global PV industry.
JinkoSolar to give TOPCon patents to rivals in exchange for licensing fees
JinkoSolar is offering its n-type tunnel oxide passivated contact (TOPCon) patents to competitors to encourage technological development and prevent legal conflicts.
Emmvee to supply 300 MWp of solar modules to KPI Green Energy
Emmvee Photovoltaic will supply 300 MWp of bifacial mono PERC panels for KPI Green Energy’s solar park in the Khavda village of Gujarat.