Blueleaf, Jakson partner for 1 GW of solar projects in Rajasthan
Blueleaf Energy and Jakson target to jointly develop over 5 GW of renewable energy projects in India. The first project under the partnership is a 1 GW solar portfolio in Rajasthan, which benefits from 25-year power purchase agreements secured with the Solar Energy Corp. of India, NHPC, and Rajasthan Urja Vikas Nigam Ltd.
Acme Solar Q3 net profit 152% up YoY
Acme Solar has reported consolidated revenue of INR 401 crore and consolidated net profit of INR 112 crore for the quarter ended Dec. 31, 2024.
Enfinity Global secures connectivity for 2 GW of solar and wind projects in India
Enfinity Global has secured connectivity for 2 GW of utility-scale solar PV and wind projects in Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Karnataka
Acme Solar secures PPA with NHPC for 680 MW renewables storage project
Acme Solar has secured a power purchase agreement (PPA) with state-owned NHPC Ltd for a firm and dispatchable renewable energy (FDRE) project of 680 MW capacity.
U.S. solar installations to drop 30% in 2025, said EIA
After a record 37 GW of new solar added in 2024, the Energy Information Administration expects 26 GW in 2025 – and even less in 2026.
Teralight switches on Israel’s largest solar plant
Teralight has activated Israel’s biggest PV project, the 150 MW Ta’anach 1 array, which will produce 310 GWh of energy per year. The facility will be expanded next year with the 104 MW Ta’anach 2 installation, featuring 440 MWh of energy storage.
Larsen & Toubro one of preferred EPC partners for 5 GW/19 GWh solar-plus-storage project in Abu Dhabi
Larsen & Toubro has been selected by Masdar as one of the preferred engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contractors for its 5 GW/19 GWh solar-plus-storage project in Abu Dhabi.
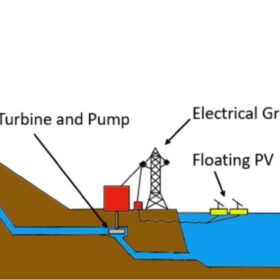
The case for combining pumped-hydro storage with floating PV
Researchers in Italy have analyzed the techno-economic viability of enhancing three pumped hydro plants in Italy with floating PV on the lower basin. They say that, with their wide results, consequences could be extrapolated to similar regions.
BC Jindal Group’s JIRE bags 180 MW solar-plus-storage project from NHPC
BC Jindal Group has announced that its renewable energy arm, Jindal India Renewable Energy (JIRE), has won a 180 MW solar plus storage project from state-owned NHPC. The project is part of NHPC’s 1,200 MW inter-state transmission system-connected solar power projects tender with 600 MW/1200 MW energy storage systems. JIRE has bagged 180 MW of […]
NTPC Renewable Energy wins 300 MW solar with storage project in NHPC’s tender
NTPC REL secured a capacity of 300 MW at a tariff of INR 3.09/kWh. The project will include the establishment of an energy storage system with a capacity of 150 MW/300 MWh.