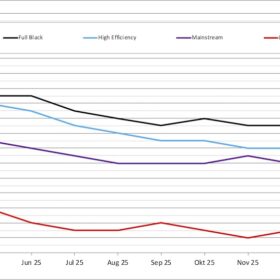
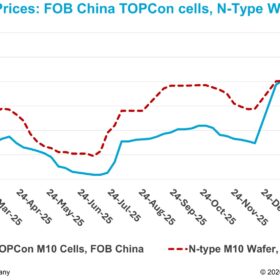
JinkoSolar achieves 26.1% efficiency for n-type TOPCon solar cell
JinkoSolar has set another world record for n-type solar cell efficiencies with its TOPCon technology, this time reaching 26.1%. The new record was confirmed by China’s National Institute of Metrology.
Sodium-ion battery anode made from toxic hogweed
Russian researchers have transmuted poisonous Sosnowsky’s hogweed into high-grade anode material for sodium-ion batteries. The obtained material has a Coulombic efficiency of 87%, which is on par with the best reported results for hard carbons synthesized from other raw materials.
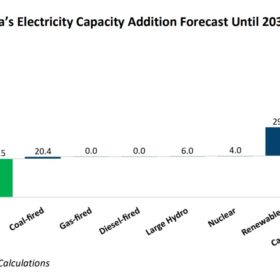
India expected to annually deploy 35-40 GW of renewables until FY2029-30 end
Ambitious government targets and commitments by both private and state-owned companies will propel renewable energy installations.
“n-type module launch reflects our commitment to India”
China’s Trina Solar has shipped more than 8 GW of solar modules to India. It is looking to strengthen its foothold in the market with the launch of n-type PV modules.
Sterling and Wilson wins $268.75 million solar order from NTPC REL
Sterling and Wilson Renewable Energy has secured the contract to install, commission, and provide three-year operation and maintenance support for a 1,255 MW AC (1,568 MW DC) solar PV project in Gujarat.
AE Solar unveils n-type TOPCon solar modules with 22.2% efficiency
Germany-based AE Solar said its new panels have a temperature coefficient of -0.35% per degree Celsius and come with a 30-year power output guarantee for 87.4% of the initial yield.
Avaada signs $2 million robotic cleaning deal with Airtouch Solar
Indian developer Avaada Group has selected Israeli robotic cleaning specialist Airtouch Solar for the maintenance of PV modules at its solar farms in Rajasthan and Maharashtra. The robotic cleaning contract between the two companies is pegged at around $2 million.
NLC tenders 300 MW of solar in Rajasthan
The state-run thermal energy giant has invited bids to install and commission 300 MW of grid-connected solar projects in Rajasthan. Bidding closes on November 11.
REC places order for Maxwell’s HJT solar line
Maxwell Technologies will supply 600 MW of manufacturing equipment for REC’s latest heterojunction (HJT) innovation, REC Alpha Pure-R.
Tata Power targets 10 GW of renewables portfolio in Rajasthan in next five years
Tata Power is looking to expand its renewable power portfolio in Rajasthan to 10 GW in the next five years, from around 5 GW at present. It will also set up solar manufacturing units in the state.