RSWM partners with Adani Energy Solutions for 60 MW renewable energy supply to its plants
Textile manufacturer RSWM has signed an agreement with Adani Energy Solutions Ltd. (AESL) for supply of 60 MW of renewable energy to its manufacturing facilities across Rajasthan. The power will be supplied from a group captive project.
AGC, NPC developing new PV cover glass recycling tech
The Japanese companies announced a partnership to advance the recycling of solar panel cover glass for application in architectural flat glass production.
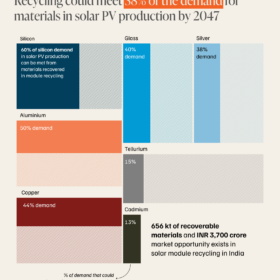
Solar module recycling offers an INR 3,709 crore market opportunity in 2047: CEEW
India is estimated to generate over 11 million tonnes of solar waste by 2047. Recycling could meet up to 38% of India’s future solar material needs.
SAEL plans INR 4,575 crore IPO; files draft papers with SEBI
SAEL Industries Ltd has filed its Draft Red Herring Prospectus with market regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to raise up to INR 4,575 crore through initial public offerings.
Solis launches 125 kW hybrid inverter for C&I solar applications
Launched under the S6-EH3P series, its 125 kW smart string hybrid inverter for C&I solar systems integrates battery smart charging/discharging (PCS), PV inversion, on-grid/off-grid and genset switching (STS), and a smart energy management system into a single compact unit.
Saatvik Green Energy secures INR 299.40 crore solar module order
Saatvik Green Energy has secured orders aggregating to INR 299.40 crore for supply of n-type TOPCon solar PV modules. The supply of modules is scheduled from Dec. 2025 to March 2026.
Researchers develop antimony-doped n-type silicon ingots to enhance solar module mechanical strength
An international team is proposing to use antimony-doped Czochralski-grown silicon as an alternative to n-type silicon for photovoltaic applications. Their analysis showed that 140 μm as-cut planar antimony-doped wafers exhibit slightly higher mechanical strength compared to common wafers doped with phosphorous.
First Solar plans fifth US factory with 3.7 GW capacity addition
First Solar will build a fifth US module plant with 3.7 GW of annual output, lifting its total domestic capacity to more than 14 GW by 2026 and reinforcing its position as the country’s largest solar manufacturer.
ANIL reports 2.4 GW solar module sales in first half of FY26
Adani New Industries Ltd (ANIL) has reported 2,443 MW of solar PV module sales for the first half of fiscal year 2026 (H1 FY26), up from 2,380 MW in the same period last year (H1 FY25).
Rethinking transformer design for the energy transition
With renewables’ share in power generation expected to grow significantly, there will also be a push in the demand for next-generation transformers that are capable of handling the intermittent nature of solar, wind, and other non-polluting sources of energy. The grid of the future demands not only more transformers but smarter, adaptive, and sustainable designs that can support India’s ambitious renewable targets and fast-rising power demand.