Global cadmium telluride solar module manufacturing capacity could reach 100 GW by 2030
In a perspective paper in Joule, a group of U.S. researchers described technology and supply chain efforts required to reach worldwide annual cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar PV capacity of 100 GW by 2030.
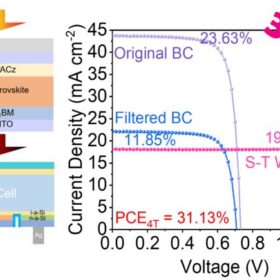
Chinese scientists build 31.13%-efficient perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell via 2D seeding agent
Researchers in China developed a novel two dimensional (2D) seeding agent to regulate crystallization in a 1.80-eV wide-bandgap perovskite film. A perovskite-silicon tandem device made with the resulting optimized subcell achieved an efficiency of 31.13%, outperforming a control device.
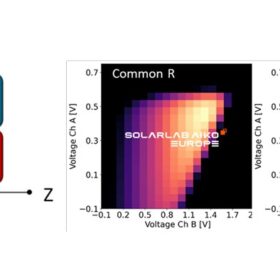
Aiko achieves 34.76% efficiency for 2-terminal perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell
The Chinese manufacturer said its 2-terminal 34.76%-efficient perovskite-silicon tandem lab-scale cell is based on heterojunction technology and developed by a collaboration of Solarlab Aiko Europe, Aiko headquarters, and its R&D in Yuwi, China.
Sinovoltaics releases new PV inverter manufacturer financial stability ranking
The quality assurance firm updated its inverter manufacturer financial stability ranking with Kstar Science and Technology, APSystems and Delta Electronics in the top three spots. It reported 19 manufacturers showing “strong financial resilience” based on Altman-Z scores.
Sinovoltaics updates solar module manufacturer financial stability ranking
The quality assurance provider reported India-based Insolation Energy, Waaree Renewable Technologies, and Solex Energy retained the top three positions in its Altmann-Z score-based quarterly ranking. Its analysts noted the number of companies with healthier scores increased from 9 to 11.
NTU achieves high stability in 25.1%-efficient inverted perovskite solar cell
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University have demonstrated a method to integrate chemically inert low-dimensional interface materials into the fabrication of inverted perovskite solar cells. Their prototype solar cells retained over 93% of the initial power conversion efficiency of 25.1% after 1,000 hours of operation, and 98% after 1,100 hours at 85 C.
AGC, NPC developing new PV cover glass recycling tech
The Japanese companies announced a partnership to advance the recycling of solar panel cover glass for application in architectural flat glass production.
Researchers develop antimony-doped n-type silicon ingots to enhance solar module mechanical strength
An international team is proposing to use antimony-doped Czochralski-grown silicon as an alternative to n-type silicon for photovoltaic applications. Their analysis showed that 140 μm as-cut planar antimony-doped wafers exhibit slightly higher mechanical strength compared to common wafers doped with phosphorous.
French startup launches cleaning robots for solar PV shade structures
Solar panel cleaning equipment company Objectif Drone has launched a new 7 kg dual-brush cleaning robot with a speed of 5 km/h made for small and medium-sized PV installations.
KAUST explores polymer alternatives to glass for solar panel covers
Researchers at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have published a review that looks at polycarbonate sheets as an alternative to solar cover glass. Their findings indicate that this new materials have a combination of low weight, mechanical strength, optical transparency, and thermal resistance that is worthy of further investigation.