India to emerge as global renewable energy powerhouse, says power minister
The nation is also set to emerge as one of the largest solar module manufacturers. It has considerable existing solar manufacturing capacity and is constructing even larger capacities, including polysilicon.
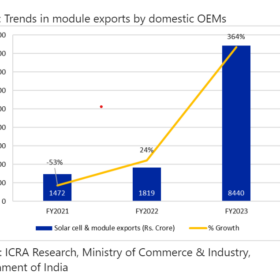
India’s solar PV module exports surge 364% YoY
India exported solar PV cells and modules worth INR 8,440 crore in FY 2022-23. USA was the top destination with a 97% share.
Solar module prices, auction volumes, and the outlook for capacity addition
Timely scale-up in tendering activity and moderation in solar PV cell and module prices, if sustained, would support improvement in capacity addition in the renewable energy sector.
India to add 20 GW of renewable energy capacity in FY2024, says ICRA
ICRA expects India to add 16 GW of solar power generation capacity, 2 GW of wind and another 2 GW from hybrid projects in FY2023-24.
Strong policy focus needed to drive pumped storage development
Despite being a mature and largely indigenous technology, pumped storage hydropower’s operational capacity in India remains very low at 3.3 GW because of the high development costs and inherent challenges in constructing these schemes.
India will require INR 9 trillion capex to meet 2030 green hydrogen target
A new report says India will require INR 5.5-6 trillion to create 115-125 GW of renewable energy capacity and INR 3-3.5 trillion to meet 35-40 GW of electrolyzers requirement in order to reach green hydrogen production capacity of 5 MMT per annum by 2030.
Relaxation of ALMM order a near-term positive for solar power developers, says ICRA
The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy has exempted solar projects to be commissioned till March 31, 2024, from the requirement to source modules from the Approved Models and Manufacturers (ALMM) list. The move provides developers with the flexibility to source modules at the most cost-competitive rates.
Battery cell manufacturing in India could attract over $9 billion in investment by 2030, says ICRA
A new report by ICRA says rising electric-vehicle penetration will drive significant investment in battery cell manufacturing in India. It expects EV battery demand in the nation to touch 15 GWh by 2025 and 60 GWh by 2030.
Amended Energy Conservation Bill to drive renewables adoption
The amended Energy Conservation Bill sets a minimum usage clause for non-fossil fuel by high carbon-emitting sectors such as power, transport, industry, and buildings. It also includes provisions to incentivize decarbonization efforts by allowing carbon trading.
Solar module price increases to affect returns on 4.4 GW of solar
Solar cell and module prices have increased by more than 40% over the last 18 months, driven by polysilicon prices. However, bid tariffs has remained lower than what is needed to mitigate the rise in module prices. The risk of lower returns is significant for 4.4 GW of projects that have been awarded over the past 18 months, with tariffs below INR 2.2 ($0.028)/kWh.