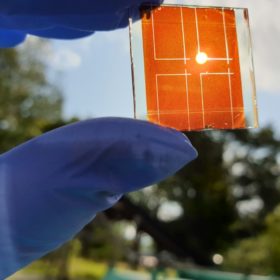
Even if organic PV is cheap enough, efficiency does matter
A British-German research team claims that organic PV technologies may become mature enough to compete with crystalline silicon and thin-film products not only in BIPV, but also in power generation in the electricity market. In order to get there, however, organic PV products will have to achieve higher efficiencies.
TERI partners Norway’s Greenstat for Centre of Excellence in hydrogen
The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the India arm of Norwegian energy company Greenstat to set up a Centre of Excellence for hydrogen in India and accelerate deployment of hydrogen technologies in the country.
New tech to apply perovskite thin-film layers to conventional solar panels
According to its creator, Swedish start-up Evolar, the new technology can be applied to existing production lines for crystalline silicon modules and increase a product’s efficiency by around 5%.
Second-life energy storage winner in EDF’s startup contest
Bangalore-based Nunam—which enables second life for used lithium-ion battery cells—is the winner of Pulse India competition conducted by French energy giant EDF. The EDF contest aims at supporting Indian startups committed to developing low-carbon and sustainable energy solutions.
The long read: Whipping up inertia
Once a natural phenomenon – a fortuitous byproduct of thermal generation – the weaning off of coal has made the emulation of inertia a priority for grid operators. It will be a few more years in most markets before a solution becomes needed with any great urgency. However, some markets have needed to come up with solutions – are they a portal into the future of grids dominated by renewables and power electronics?
Thermal energy storage system goes online at IIT Kanpur
The thermal energy storage system with a 775 tonnes-of-refrigeration heat rate is installed at IIT Kanpur’s Centre for Environmental Science and Engineering building. It is part of an urban pilot under a joint Indo-US project called UI-ASSIST on Smart Grid and Storage Technology.
PV powered desalination is “the most competitive design”
Scientists in France conducted an analysis on the competitiveness of water desalination, taking a large scale project planned for Morocco as a case study. The research concludes that PV without storage is the cheapest option to power desalinators, and will likely remain so until at least 2030.
Indian researchers create bio-inspired algorithm for MPPT optimization
Indian researchers have created a hybrid salp swarm algorithm to optimize MPPT tracking in PV systems under partial shading conditions. It is based on the swarming behavior of salps in the ocean.
IndianOil turns to gas, not green hydrogen, to reduce Delhi bus emissions
The public sector energy company has opened a compact reformer plant at Delhi Transport Corporation’s Rajghat bus depot. The facility will produce hydrogen-enriched compressed natural gas as a bus fuel. A trial period will see 50 gas-powered buses run on the blended fuel with fuel economy and emissions monitored.
Ministry drafts policy for rural solar appliance roll-out
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy is eager to ramp up deployment of solar-powered dryers, cold storage and charkhas across the nation’s 600,000 villages.