Avaana Capital draws first tranche of Green Climate Fund’s $24.5 million commitment
This marks Green Climate Fund’s first venture capital investment in India’s deep-tech ecosystem.
Tata Elxsi, Infineon partner to develop ready-to-deploy EV solutions
The partnership focuses on developing scalable battery management systems, bi-directional onboard chargers and other EV systems for two-wheelers, three-wheelers, passenger vehicles, and commercial vehicles in the Indian market.
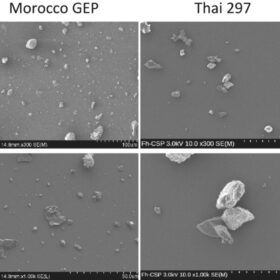
Different dust, different impact on PV module performance
Scientists in Germany have collected dust from Qatar, Morocco and Thailand to analyze the impact on the performance of uncoated solar glass and uncoated PV mini-modules. Their analysis has shown that dust coverage could range from 4% to 60%.
Understanding P50, P90, and P99 in solar energy
In the solar energy sector, P50, P90, and P99 represent the probability that a project will generate at least a certain amount of electricity in a given year. This article explains what these probabilities mean, why they are important, how they are calculated, and how to use them.
Indian scientists build 29.14%-efficient tandem solar cell with inverted top perovskite device
The researchers said they optimized the low-bandgap inverted perovskite cells through a passivating aluminum oxide (Al2O3) interlayer deposited via atomic layer deposition (ALD), which significantly helped improve device efficiency.
Hygenco breaks ground on green ammonia plant in Odisha
Strategically located at the Gopalpur port hub, the plant will meet both domestic and global demand for green ammonia—enabling decarbonization across key industrial sectors.
Perovksite-TOPCon tandem solar cell based on self-assembled monolayer achieves 31.1% efficiency
Researchers in China have fabricated a perovskite-TOPCon solar cell with a top perovskite device utilising a self-assembled monolayer aimed to improved cell stability. The tandem cell achieved a high fill factor and a certified efficiency of 30.9%.
The Hydrogen Stream: ACME Group reaffirms green hydrogen project in Odisha
ACME Group has reaffirmed its commitment to establish a green hydrogen and ammonia project in India at Gopalpur, Odisha. The project, to be set up within Tata SEZ, will produce 400,000 tonnes of green ammonia annually.
MIT-WPU launches battery research center focused on advanced Li-ion and Na-ion technologies
The facility supports comprehensive end-to-end battery development, from active material synthesis to coin cell fabrication, and electrochemical performance evaluation.
The hydrogen stream: Honeywell, NTPC Green join hands for production of sustainable aviation fuel
The collaboration will leverage Honeywell’s eFining technology to produce sustainable aviation fuel from carbon dioxide (CO2) feedstock captured from NTPC’s power plants and green hydrogen.