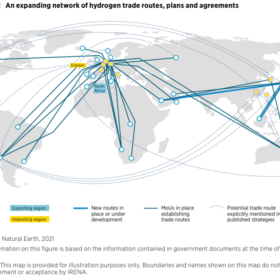
Green hydrogen could disrupt global trade, bilateral energy relations
While there are still many uncertainties as to the way in which hydrogen trade might evolve and change economic ties and political dynamics between countries, experts agree that green hydrogen can bring winds of change to the global energy arena. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, significant geoeconomic and geopolitical shifts are just around the corner.
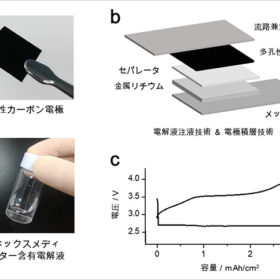
Japanese consortium builds lithium-air battery with energy density of 500 Wh/kg
A Japanese group has developed a storage system with potential applications in residential storage, electric vehicles, drones and Internet-of-Things devices.
Panasonic unveils 410 W solar panel with 22.2% efficiency
The new heterojunction module series is compatible with Panasonic’s Evervolt battery and has a power output ranging from 400 to 410 W. It also features a temperature coefficient of -0.26% per degree Celsius.
The long read: Dealing with dust
Sand and dust are a PV plant operator’s worst nightmare. Performance losses due to soiling, or “the dust effect,” are a cause for innovation among O&M providers, particularly in dry and dusty regions that are otherwise ideal locations for large-scale solar installations. Yazeed Al-Mousa examines the latest robotic cleaning solutions, as well as the software and sensors that help plant operators with the tricky economic decision of when to actually start cleaning.
Residential building fully reliant on hydrogen for space heating, hot water
The campus of the Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in the Netherlands is currently hosting a retrofitted existing building provided with heating by an H2 heating boiler in the attic. The boiler is linked to an underground hydrogen system.
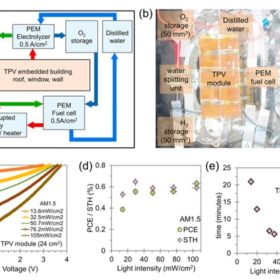
Solar-powered hydrogen for domestic applications via building-integrated transparent platform
An international research group has created a closed-loop, transparent energy platform based on PV power generation and hydrogen production from photo-electrochemical cells. The system is claimed to supply power without interruption and to be transparent enough to be integrated into buildings.
The long read: Finding PV faults faster
PV cell and module manufacturers are increasingly turning to artificial intelligence to monitor production lines and the products coming off them in minute detail. As inline monitoring and testing equipment become more sophisticated, cell and module makers must be prepared to manage the enormous amounts of data and pull out the points that will save them time and money. pv magazine examines the software solutions backing state-of-the-art PV production.
SmartHelio appoints key executives
The Swiss PV diagnostics and predictive solutions provider has appointed Neeraj Dasila as chief technology officer (CTO), and Shankaransh Srivastava as vice president-marketing.
Electrolyzer tech to produce hydrogen from seawater
With a new start-up and a consortium in the Netherlands, German automotive supplier Schaeffler wants to significantly reduce the costs of green hydrogen.
Hero Future Energies, Ohmium to install 1 GW of green hydrogen capacity
Indian renewable energy developer Hero Future Energies has partnered with US-based Ohmium International on the development of green hydrogen plants in India, the UK, and Europe with a cumulative electrolyzer capacity of 1 GW.