JSW Energy to re-organize renewable and thermal businesses
The private-sector power producer will group its renewable energy business under wholly-owned arm JSW Neo Energy as it targets growth in renewable energy generation, energy storage, and green hydrogen business.
Adani Solar partners KSL Cleantech for retail expansion to East and Northeast
The Indian solar manufacturer and EPC contractor has chosen KSL Cleantech as the channel partner for the retail distribution of its solar panels in the eastern and northeastern markets of India.
The energy storage decade has arrived, BNEF says
Falling battery costs and “surging” renewables penetration make energy storage a “compelling flexible resource in many power systems.”
Chile wants to export solar energy to Asia via 15,000km submarine cable
The Antípodas project was announced by the Chilean government last week. It is aimed at taking advantage of the huge solar potential of the Atacama Desert, which is the world’s region with the highest solar radiation.
Adani Green targets 45 GW renewable energy generation capacity by 2030
The renewable energy developer had an operational capacity of 5,410 MW (4,763 MW solar and 647 MW wind) as of September 30.
US Commerce Department throws out anti-dumping petitions
The dismissal is a win for the Solar Energy Industries Association, which vigorously opposed the request by American Solar Manufacturers Against Chinese Circumvention (A-SMACC) for anti-dumping and anti-circumvention (AD-CVD) tariffs
IndianOil to install EV charging facilities at 10,000 fuel stations
The oil and gas major, with a current installed base of 448 EV charging stations and 30 battery swapping stations, plans to expand the charging station network in a phased manner over the next three years. The first phase will focus on nine cities, including Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Kolkata, Surat, and Pune.
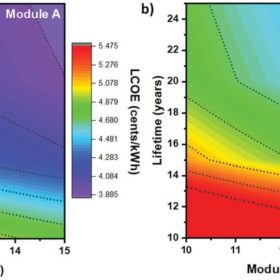
Analyzing the opportunity for perovskite solar module production in India
Scientists in India conducted a techno-economic analysis for a 100 MW production line for carbon-electrode perovskite solar modules, located in Himachal Pradesh, India. The analysis concludes that, even at the smaller scale, this emerging technology could achieve cost levels comparable with today’s silicon solar products.
Sungrow hits 10 GW of solar inverter shipments in India
The Chinese inverter company has shipped more than 10 GW of solar inverters in India since it began its operations in the market in 2014.
China power crisis hits Indian solar projects
After the ravages of Covid-19, electricity shortages in China have now raised costs for its solar manufacturers, with knock-on effects for developers in India too, again highlighting the dangers of relying on a single solar supply chain.