Rs 900-billion package not a solution to Discoms’ woes, but offers respite
For long-term stability, Discoms need to address operational issues like low billing and collection efficiency and high aggregate technical and commercial losses.
Innovation promises cheaper solar cell glass manufacturing
Indian scientists have developed a hybrid production method combining metal mesh and a metal-oxide layer over a glass substrate which they say brings down production cost by 80% compared to the tin-doped, indium oxide-based technology currently in use.
Solar tariffs below Rs 2.55/kWh financially unviable now, says Ieefa
To earn reasonable returns on solar projects, developers must factor in the various risks and correctly estimate the cost of every component before bidding.
Solar EPC firm SunEdison raises US$2.5 million from US investor
Fenice Investment Group will subscribe to compulsorily convertible preference shares (CCPS) of SILRES Energy Solutions at Rs 10 per CCPS. The investment is expected to complete by May 25.
Liquidity booster for Discoms, state guarantee to rescue
The government’s announcement of Rs 90,000 crore liquidity injection comes as a relief for Discoms. It will be, however, essential to see as to what extent the discoms can avail the scheme given the ‘tied’ nature of this support and requirement of State Government guarantee—shares Care Ratings.
Gujarat announces sops to attract new manufacturing units
Plug-and-production facilities and labour law exemptions for 1200 days are among the decisions announced by the chief minister of the Indian state which contributes 7.9% to India’s gross domestic product and 20% to the overall exports.
Gigawatt scale ‘ultra-mega’ solar parks driving India’s energy transition
India hosts numerous 1 GW-plus solar parks, two of which are the largest commissioned in the world. The huge sites have been instrumental in driving economies of scale and continue to attract global capital and some of the most recognized renewables developers.
Covid-19 can impact electric vehicle demand
Industry body FICCI has recommended an extension of the FAME II Scheme by at least one year to 2023 as it feels change in the consumer behavior can impact the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) in the short term.
EU, India invite joint research proposals on integrated local energy systems
The projects shall be co-funded by India’s Department of Science & Technology and the European Commission’s Innovation and Networks Executive Agency. The aim is to make energy supply cleaner, more efficient and affordable by smartly integrating large amounts of renewable energy in local energy systems. Proposals can be submitted till September 1.
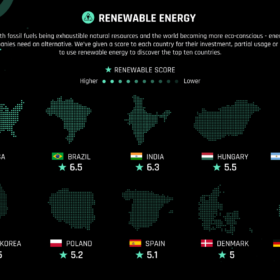
India ranks third on renewable energy investment
The country earned a score of 6.3 on a 10-point scale on the basis of its investment, partially usage or plans to use renewable energy in the near future—in a study by UK based analytics firm British Business Energy. The USA ranks first with a score of 7, followed by Brazil at 6.5.