Corporate renewable power procurement: Global models and their suitability for India
Commercial and industrial (C&I) sector consumes 51% of the total electricity generated in India, with a mere 3% of this consumption coming from renewable energy. To increase renewable energy uptake among C&I consumers, India needs to explore new models like virtual power purchase agreements, green tariffs, internationally tradable RECs that have already been successfully tried and tested in many countries—according to a report by climate advocacy group WWF India.
India and German development lender to launch rooftop solar scheme
Program aims to drive down the cost of solar electricity to a maximum of Rs2.50/kWh in a nation where tariffs vary wildly from state to state.
FAME India so far
The government has supported 425 electric buses on pilot basis since the launch of FAME India [Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles in India] scheme that—in its second phase—aims to support (through incentives) about 7000 e-buses over a period of three years commencing from April 1, 2019.
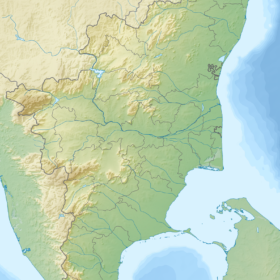
$451 million ADB loan to strengthen power connectivity in Tamil Nadu
The investment will be used to establish an extra-high-voltage transmission link between Virudhunagar and Coimbatore to transfer the additional generation capacity of 9 GW, including 6 GW from renewables, by 2025 to meet the increased power demand in the Chennai–Kanyakumari Industrial Corridor.
Distributed Energy’s rooftop solar aggregator platform raises Rs 100 million funding
The platform connects credible renewable energy projects with investors, and has already delivered 5 MW of energy to a range of companies in Southern India and Rwanda.
ADB extends $250 million loan to EESL for energy efficiency initiatives
The investment—part of a $592 million assistance package—will be used to promote adoption of smart meters, distributed solar photovoltaic systems and e-vehicles in India.
Government in the process of finalizing new energy policy: NITI Aayog Additional Secretary
Apart from thrust on energy efficiency and clean energy, the new policy will focus on Make in India for cells used in electric vehicle batteries and measures for demand creation and incentivizing investments.
Clean energy investment in developing nations slumps as financing in China slows: BNEF
Clean energy investment across 104 emerging markets fell sharply by $36 billion in year 2018 from the previous year, even as their coal burn surged approximately 500 terawatt hours to a record high of 6.9 thousand terawatt-hours. Though the decline in clean energy investments was driven largely by China, inflows to India and Brazil also slipped by $2.4 billion and $2.7 billion, respectively. India, however, emerged as the market with greatest renewables potential.
DST calls for Indo-Israel joint research on solar energy and storage
December 5 is the last date to submit proposals for the joint research program on advanced materials for next-generation solar energy utilization and energy storage that will sponsor around 10 projects. The maximum funding available for all research projects approved is Rs40 million for the Indian side and 4,000,000 NIS for the Israeli side, for a period of two years.
‘The right vision is needed to unleash the potential of floating PV in India’
The technology brings environmental, economic and social benefits, says the senior VP of Ciel et Terre’s Indian business. However, the nation’s obsession with price dictating business decisions, he adds, ignores the truism that ‘in the long run, cheap products lead to more cost’.