NTPC Green announces 250 MW Kadapa solar project in Andhra Pradesh fully operational
The 250 MW solar project in Kadapa district of Andhra Pradesh is now fully operational following the commercial operation of the remaining 91.6 MW capacity.
“Multi-dimensional renewable energy growth key to India’s long-term development and energy security”
India’s renewable energy expansion will extend beyond utility-scale projects to distributed renewable energy, green open access and emerging prosumer models enabled by digital platforms and the India Energy Stack as the nation advances toward its vision of becoming a developed nation by 2047.
ABB invests further $75 million to expand manufacturing and R&D footprint in India
ABB will invest a further $75 million in India during 2026 to significantly expand its manufacturing and research and development (R&D) capabilities for critical electrification and automation solutions.
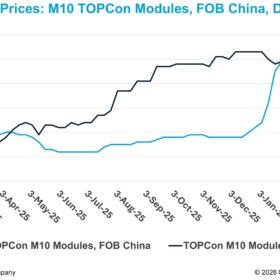
The strategic turn in industrial energy procurement
Industrial energy procurement has broadened in scope. Tariffs remain an important part of the decision, alongside a wider set of considerations. Buyers now weigh reliability, predictability, sustainability, and long-term exposure alongside price.
The limits to growth: The Malaysian way of navigating the data centre boom
Malaysia’s rising power demand, driven by industrial growth and data centers, is exposing grid and capacity constraints, prompting policies like Corporate Renewable Energy Supply Scheme (CRESS) to enable corporate renewable procurement while maintaining system cost recovery. A key factor is the System Access Charge (SAC), whose uncertain future trajectory affects long-term solar PPAs and investment decisions, making scenario-based modelling crucial for assessing project bankability.
Oriana Power secures EPC contract for 234 MW floating solar plant in Jharkhand
Oriana Power has secured an INR 1,180.53 crore contract for the supply of plant and equipment, EPC, and long-term operation and maintenance of a 234 MW grid-tied floating solar PV plant at the Maithon Dam Reservoir.
Sunsure signs solar PPAs with Daeseung Autoparts, Ilgahng Automotive
Sunsure Energy has secured 8 MWp of solar power agreements to supply clean energy to the Tamil Nadu facilities of South Korean automotive companies.
Ecoflow debuts 5 kWh residential inverter battery with 100% depth of discharge
EcoFlow has unveiled the single-phase Ocean 2 all-in-one battery inverter at Key Energy in Rimini. The system features a more compact 5 kWh LFP battery stackable up to 30 kWh and offering 100% depth of discharge, 3.4 kW discharge power, and IP66 protection.
ACME Solar signs 450 MW FDRE PPA with SJVN, commissions second phase of 285 MW/600 MWh BESS project in Jaisalmer
ACME Solar has secured two power purchase agreements (PPAs) with SJVN Ltd for 300 MW and 150 MW, totaling 450 MW, under a firm and dispatchable renewable energy (FDRE) project. The company also announced the commissioning of an additional 38 MW/82 MWh at its 285 MW/600 MWh battery energy storage system (BESS) project in Jaisalmer district, Rajasthan.
Siemens Energy India Q1 profit rises 34.9% to INR 313 crore
Siemens Energy India Ltd has reported a 26% year-on-year increase in revenue to INR 1,911 crore and a 34.9% rise in profit after tax to INR 313 crore for the quarter ended December 2025 (Q1 FY2026). The company’s order backlog expanded 37.6% to INR 17,599 crore.