India installed record 21.9 GW of solar and wind capacity in H1 2025: JMK Research
The nation added 18.3 GW of solar capacity and around 3.5 GW of wind capacity during the Jan.–June period of 2025, according to JMK Research.
India installed 17.4 GW utility-scale solar, 5.15 GW rooftop PV capacity in FY 2025: JMK Research
Rajasthan led the annual solar additions with 6.5 GW, followed by Gujarat (3.6 GW) and Maharashtra (2.3 GW).
Volks Energie wins second BPCL contract for solar plus lithium battery storage project
Volks Energie will deploy a solar-plus-storage system to provide off-grid power backup for the control stations and operational infrastructure of BPCL’s Irugur-Devangonthi Pipeline project.
Crompton secures INR 101-crore solar pumps order from MEDA
Crompton Greaves Consumer Electricals has received a Letter of Award (LoA) for the design, manufacture, supply, installation, testing, and commissioning of 4,500 off-grid solar photovoltaic water pumping systems across Maharashtra under Component-B of the PM-KUSUM scheme. The turnkey project also includes a comprehensive five-year maintenance contract.
India installed 5.93 GW of utility-scale solar in Q1 2025, says JMK Research
India installed 5.93 GW of utility-scale solar capacity in Jan-Feb-March period of 2025, marking a 12.2% increase compared to the previous quarter. Additionally, around 1.34 GW was added in the rooftop solar segment during the same period.
India to reach 160 GW of solar module capacity, 120 GW of cells by 2030
A new report by SolarPower Europe, with India-specific projections contributed by the National Solar Energy Federation of India (NSEFI), projects India’s solar module manufacturing capacity to increase significantly from 80 GW in 2025 to 160 GW by 2030. Cell manufacturing capacity is projected to grow from 15 GW to 120 GW.
India installed 7.8 GW solar in Q1 2025, says IEEFA
India added 7,782 MW of solar power generation capacity in the Jan-Feb-March period of 2025, the second-highest PV installation in the last 13 quarters, according to a power sector summary by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA).
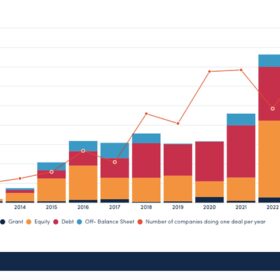
Global investment in off-grid solar down 30% in 2024
Off-grid solar investment fell 30% in 2024, with early-stage firms and productive-use tech hit hardest, says Gogla. The global association for the off-grid solar energy industry adds that scale-ups attracted 77% of the nearly $300 million invested, signaling stronger commercial viability among mature players.
India installed 24 GW solar in FY2025, says JMK Research
India installed 23.8 GW of new solar capacity in FY2025, including 16.9 GW from utility-scale, 5,148 MW rooftop and 1,785 MW offgrid installations.
Mauritius hosts SolarX Accelerator Programme in collaboration with International Solar Alliance and Business Mauritius
The two-day SolarX Accelerator Programme in Mauritius brought together 35 startups from across Asia and APAC region to accelerate the development and deployment of innovative solar solutions.