How to balance power losses, cost effectiveness in PV-BESS-driven EV charging stations
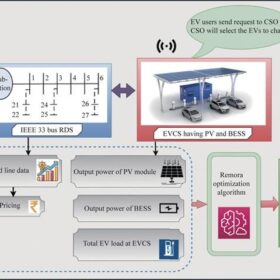
Scientists in India have developed a novel method to optimize the placement of an EV charging station on the grid, along with the size of its PV generation and battery storage. They have also created a framework for an innovative slot offering.
How homegrown players are leading the charge in green mobility
India’s journey toward electric mobility is not just about reconnecting with a global trend, it’s a movement rooted in the spirit of Aatmanirbhar Bharat and Make in India. What makes our transition extraordinary isn’t just the scale, but the fact that we’re building this transformation from the ground up.
Servotech Renewable expands solar, EV charger business to Mauritius in partnership with Enovra Energy
Servotech Renewable Power Systems has appointed Enovra Energy Solutions as its exclusive representative for the distribution and deployment of EV chargers and solar solutions across Mauritius and neighboring regions.
Charging up fleets to overcome India’s infrastructure hurdles for EV adoption
Scaling electrified fleets relies not just on vehicles, but on the infrastructure that powers them: without a robust, accessible, and optimized charging ecosystem, fleet EV adoption may stall, undermining both environmental goals and operational efficiency.
Novel MPPT technique for EV charging combined with PV, fuel cells
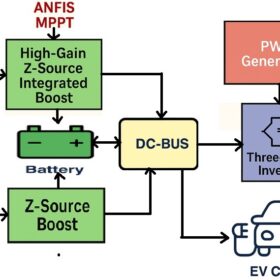
Scientists in India have designed a system that uses PV panels, a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell, battery storage, and a supercapacitor. It also relies on an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system-based MPPT that reportedly achieves an efficiency of 98.7%.
Mitsubishi, Evhacs launch world’s first integrated heat pump, EV charger
The integrated system is claimed to efficiently provide dynamic load balancing, while supporting demand-side management and future smart grid applications. The heat pump technology comes from Mitsubishi’s Ecodan, Mr. Slim, and M heat pump series, which Evhacs modified for integration with the EV charger.
Wireless electric vehicle charging tests improve efficiency by 88%
Scientists in India have simulated and tested a prototype wireless charging system for electric vehicles, with a three-port DC–DC converter at its core and have found it achieved an improved efficiency of 88%.
Electric two- and three-wheelers already cheaper to own than petrol variants: CEEW
Electric two-wheelers have a lower total cost of ownership (TCO) of INR 1.48/km than INR 2.46/km for petrol models. Three-wheeler EVs cost INR 1.28/km versus INR 3.21/km for petrol.
Servotech plans solar manufacturing, eyes global expansion in EV charging segment
Servotech Power Systems has announced plans to set up solar cell and module manufacturing facilities. The company is also looking to expand globally in the EV charging segment.
Exicom unveils new DC fast charger, built for enhanced efficiency and reliability
India’s Exicom has launched its next-generation DC fast charger, Harmony Direct 2.0, engineered for reliability and efficiency in EV charging. The charger is powered by India’s first indigenously developed EV charger controller platform.