Clean hydrogen boom by 2030, but targets remain elusive
The clean hydrogen market must navigate technological, political, and economic uncertainties to realise its full potential.
The Hydrogen Stream: GAIL opens 10 MW green hydrogen plant
GAIL (India) Ltd, India’s largest natural gas company, has set up a green hydrogen plant that can produce 4.3 tonnes of hydrogen per day through 10 MW PEM (proton exchange membrane) electrolyzer units.
Jakson Green secures INR 600 million to advance renewable energy projects
Jakson Green has secured a sustainable trade facility of INR 600 million ($7.2 million) from HSBC India. This funding will support the company’s working capital requirements for its renewable energy business, both in India and internationally.
Indian Army receives hydrogen bus
The Indian Army has received a hydrogen fuel cell bus under its collaboration with Indian Oil Corp. Ltd (IOCL) for demonstration trials of this technology. The bus promises a mileage of 250-300 km on a full 30 kg onboard tank of hydrogen fuel.
Reliance signs alkaline electrolyzer deal with Norway’s Nel
Through the agreement, Reliance gets access to Nel’s technology platform for manufacturing alkaline electrolyzers.
Policy uncertainty creates ‘gap’ between hydrogen aims and reality, says BNEF
BloombergNEF (BNEF) says in a new study of 1,600 planned hydrogen projects that governments will miss their 2030 hydrogen targets. Analyst Adithya Bhashyam tells pv magazine that most of the announced projects to the end of this decade lack the key conditions for success.
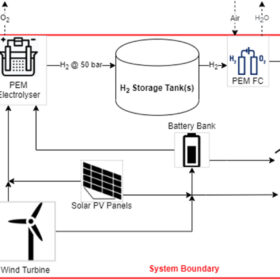
Hybrid hydrogen-battery system for off-grid PV-powered homes
Conceived by a Dutch research group, the proposed system is intended to store surplus renewable electricity via hydrogen generation and battery storage, with the latter being used only when hydrogen generation is not immediately available. Despite its high initial costs, the system can reportedly offer stable operation.
The Hydrogen Stream: Hygenco, Mitsubishi partner to deliver green hydrogen-fired GTCC power plants
Hygenco Green Energies has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Mitsubishi Power to deliver green hydrogen-/ammonia-fired gas turbine combined cycle (GTCC) power plants.
ReNew secures $1 billion from European bank Societe Generale
Societe Generale will provide up to $1 billion of debt finance and advisory solutions, over the next three years, to support the development of ReNew’s energy transition projects.
The Hydrogen Stream: India extends bidding for second round of electrolyzer incentives
Manufacturers now have until May 31 to submit bids for setting up electrolyzer manufacturing capacities in India under the second round of the government’s Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) program.