Musk proposes PV-powered AI satellite network to fight global warming
Elon Musk says a constellation of solar-powered artificial intelligence satellites could regulate the planet’s energy balance and limit global warming.
Solar tariffs kill Americans
Researchers show how solar panel imports saved nearly 600 American lives over a decade, while industry data indicates that the Suniva solar tariff may have caused more than one hundred preventable deaths.
Rethinking transformer design for the energy transition
With renewables’ share in power generation expected to grow significantly, there will also be a push in the demand for next-generation transformers that are capable of handling the intermittent nature of solar, wind, and other non-polluting sources of energy. The grid of the future demands not only more transformers but smarter, adaptive, and sustainable designs that can support India’s ambitious renewable targets and fast-rising power demand.
Pipelines for the future: Engineering challenges in hydrogen transport
As nations move towards low-carbon economies, hydrogen pipelines could become the backbone of industrial decarbonisation, linking production hubs to demand centres with efficiency, safety, and reliability. Building this backbone is not just an engineering task; it is a strategic investment in a cleaner energy future.
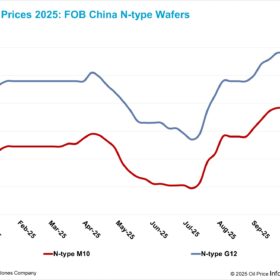
Solar wafer prices stable, with emerging downward pressure despite policy interventions
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides a quick look at the main price trends in the global PV industry.
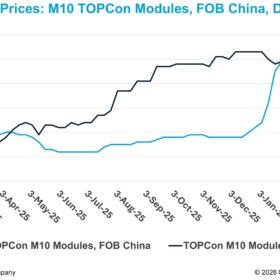
China module prices climb 1.14%, industry awaits polysilicon consolidation plan
In a new weekly update for pv magazine, OPIS, a Dow Jones company, provides a quick look at the main price trends in the global PV industry.
Batteries at the heart of India’s energy future: Building a flexible and democratic power system
As India races toward its goal of 500 GW non-fossil fuel capacity by 2030, having already reached 217.62 GW as of January 2025, integrating variable renewable energy sources requires flexible storage solutions that can bridge generation-demand gaps while maintaining grid reliability. The dramatic cost declines, technological innovations, and supportive policy frameworks have created a perfect storm for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) adoption, transforming what was once a nascent technology into a commercially viable solution driving India’s clean energy future and enabling a more flexible, resilient, and decentralized power system.
PV module recycling gains momentum as waste volumes surge globally
A comprehensive new report from IEA PVPS Task 12 reveals how countries around the world are managing the growing volumes of end-of-life solar modules, implementing regulations and scaling recycling infrastructure to handle the expected increment in PV waste over the coming decades.
How startups are driving affordable battery solutions for Bharat
With lithium being an imported raw material, recycling and repurposing of lithium batteries once they have completed their lifecycle is paramount. In line with this, Indian startups have come up with several ingenious business models for second-life applications that repurpose EV or lithium-ion batteries for stationary storage.
How India’s move to secure rooftop solar data with stricter inverter protocols will help to protect energy sovereignty
India’s decision to tighten inverter protocols and secure rooftop solar data under national jurisdiction is a critical step toward reinforcing its energy sovereignty. With ambitious rooftop solar targets already underway, these measures help ensure that growth in clean energy does not come at the cost of vulnerability in grid security, data privacy, or foreign dependence.